
Uncover Why Your Home Suddenly Smells Like a Skunk
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: There’s nothing quite like the pungent odor of skunk wafting through your home

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: There’s nothing quite like the pungent odor of skunk wafting through your home

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: It’s a common belief that your window AC unit is like a magical

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Winter is upon us, and with it comes the challenge of keeping our
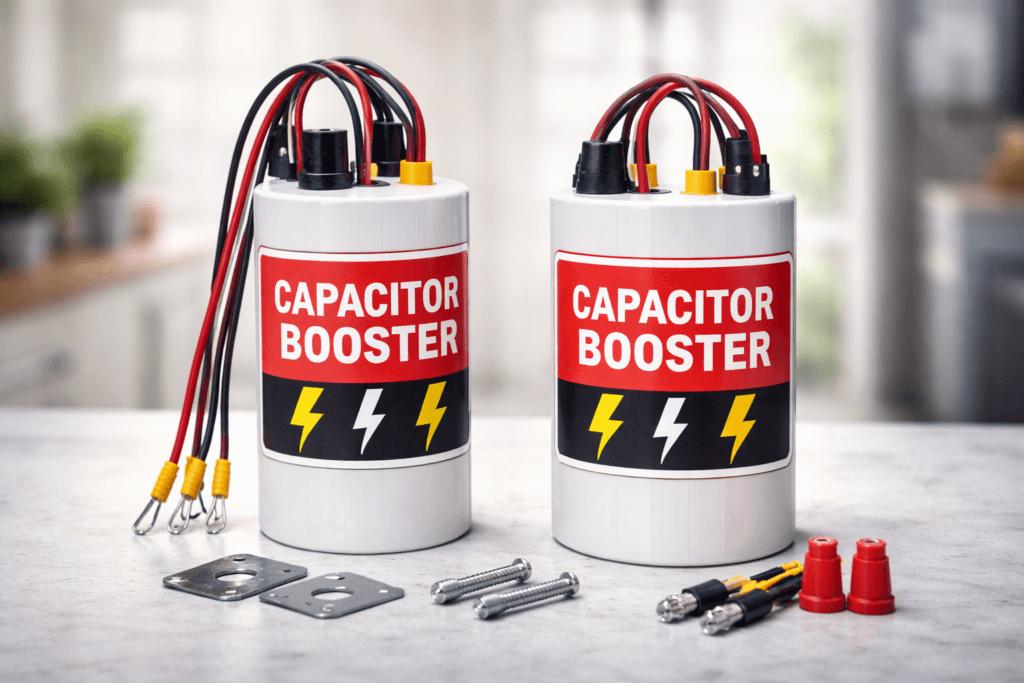
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: You’ve spent good money on a powerful car audio system, but when the

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: When the heat in Glendale rises, a working AC is essential. Fast AC

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: If you have an older home, you’ve probably noticed it: a chalky, white

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: You see a puddle of water on your utility room floor. Is it

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Before exploring specific types of AC units, it’s crucial to assess your cooling

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Air handlers are the unsung heroes of your HVAC system. They play a

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Los Angeles is known for its sunny skies and warm weather. But when

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Navigating the world of energy tax credits can be daunting. But it doesn’t

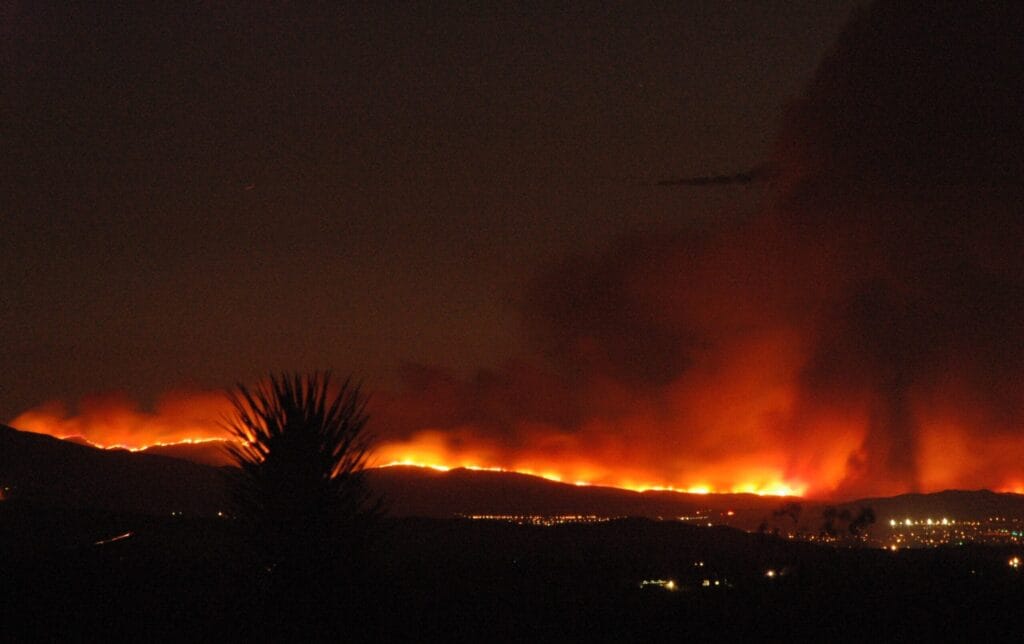
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: When wildfires like the Hurst fire rage, they leave more than just charred

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Los Angeles is known for its sunny weather, but when the heat rises,
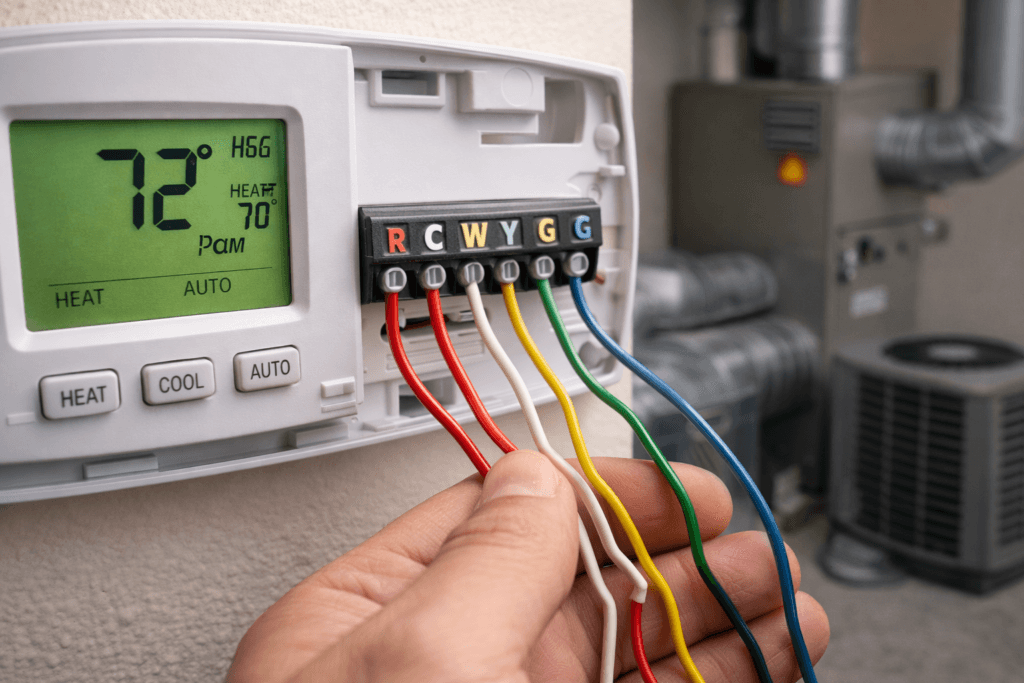
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: In today’s world, home technology continues to evolve, offering greater comfort and efficiency.
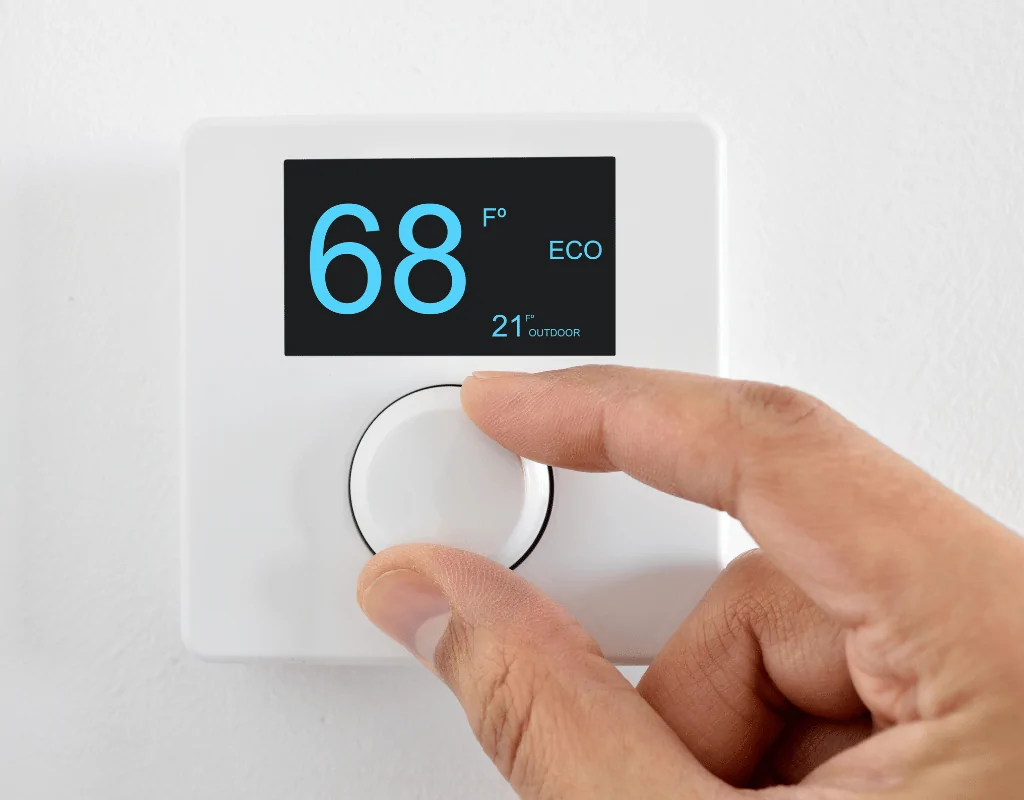

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Welcome to the future of home comfort! At LC Heating and Air Conditioning
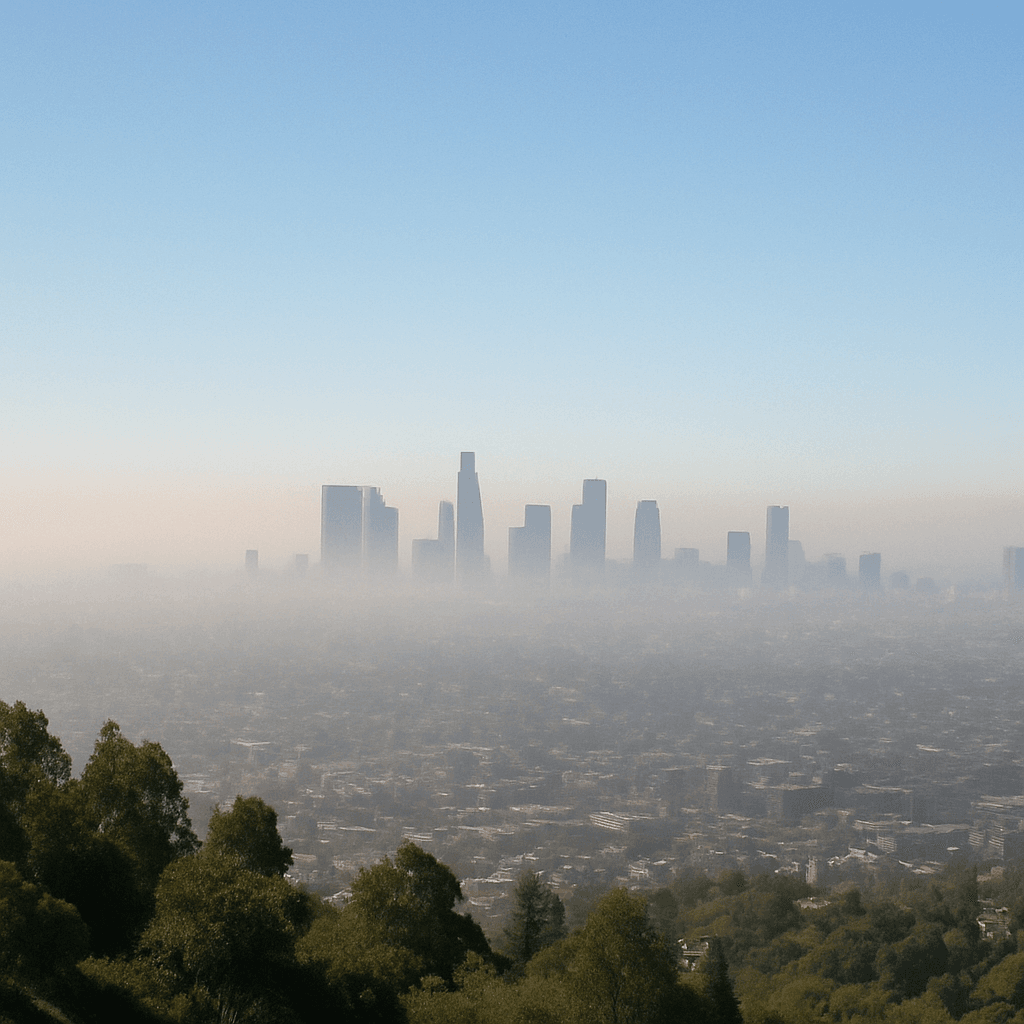

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Reducing Air Pollution in Los Angeles is an ongoing challenge that affects the
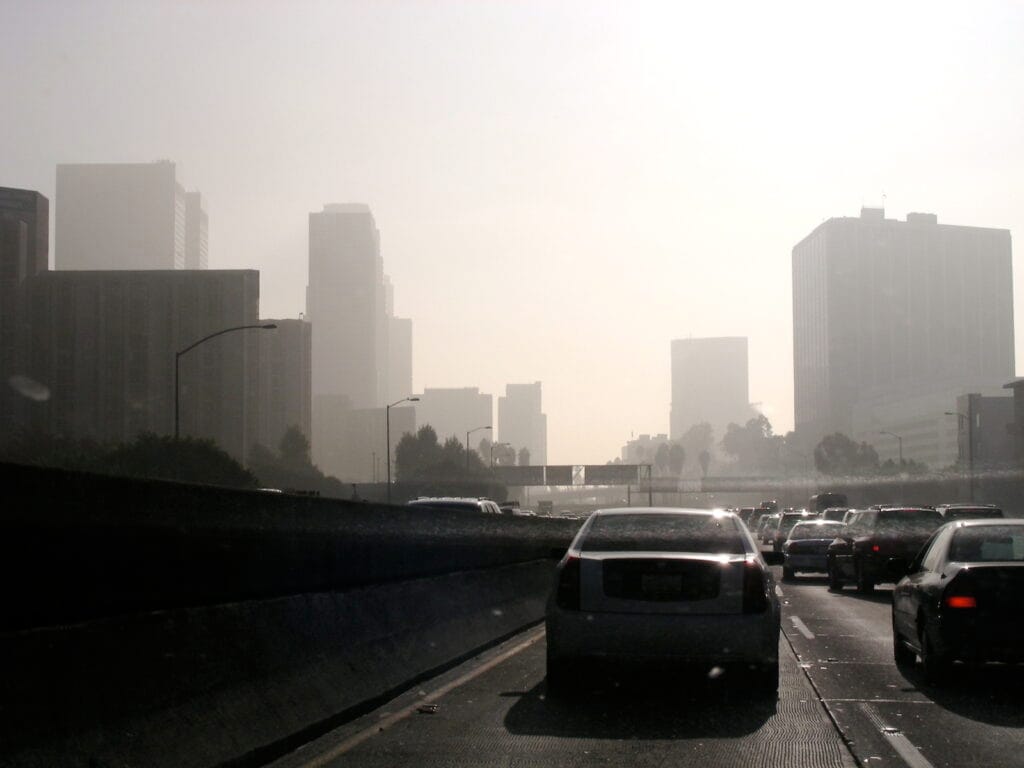

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Breathing clean air is essential for a healthy life. In Los Angeles, where
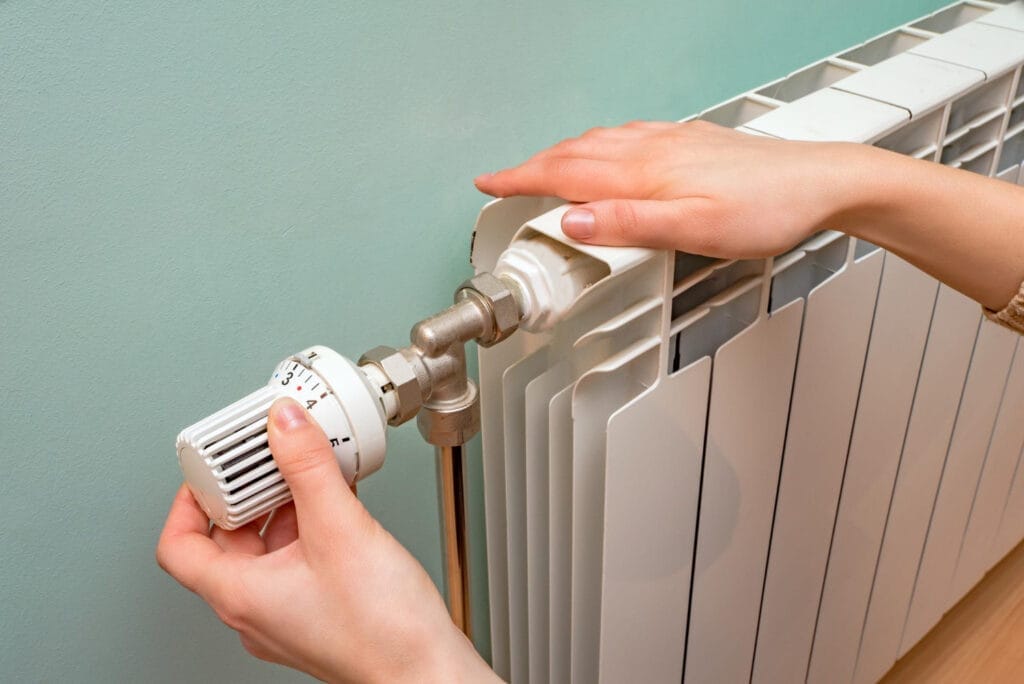

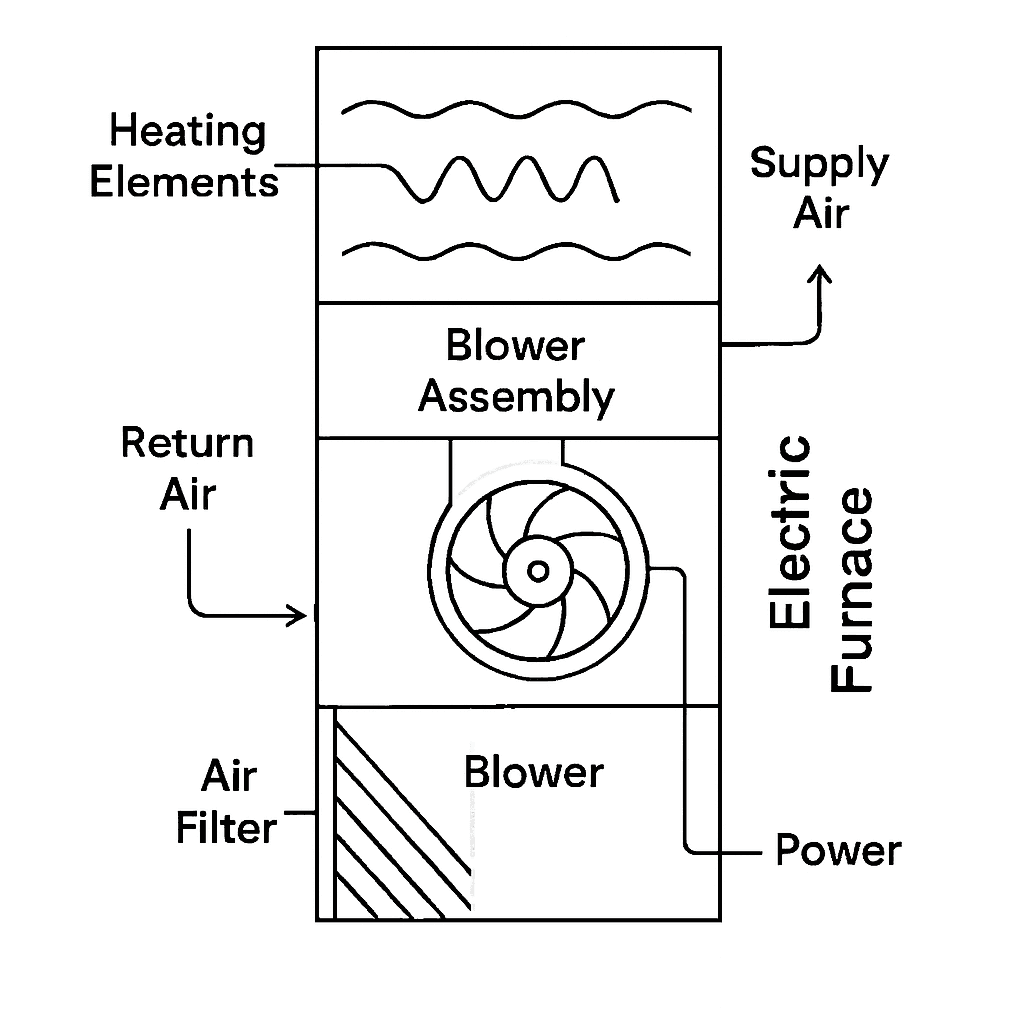
Discover how a home heating furnace operates, its fuel types, and its role in distributing warm air through your home’s central air system efficiently.
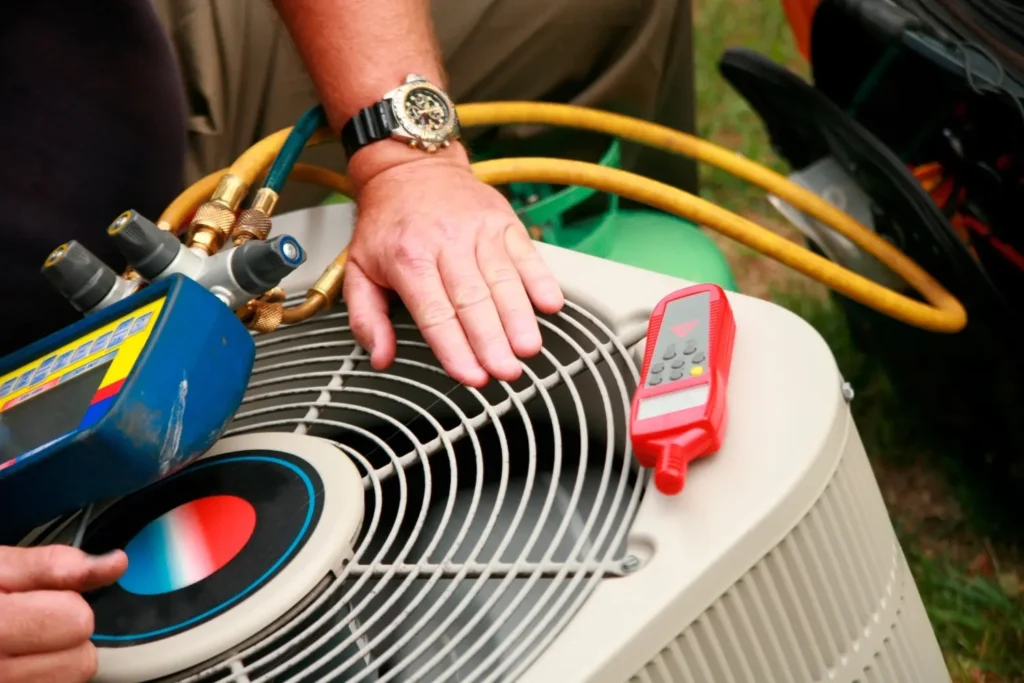

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: When it comes to construction, one term you’ll often come across is HVAC.
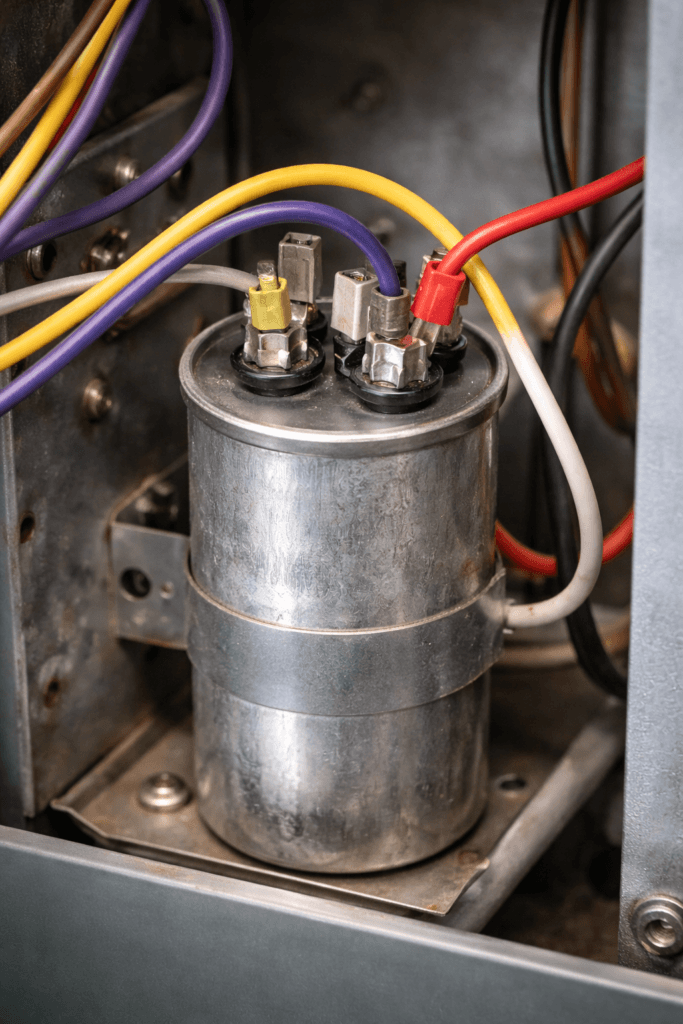
The Los Angeles heat is relentless, and your air conditioner just died. Before you panic, know this: many common AC
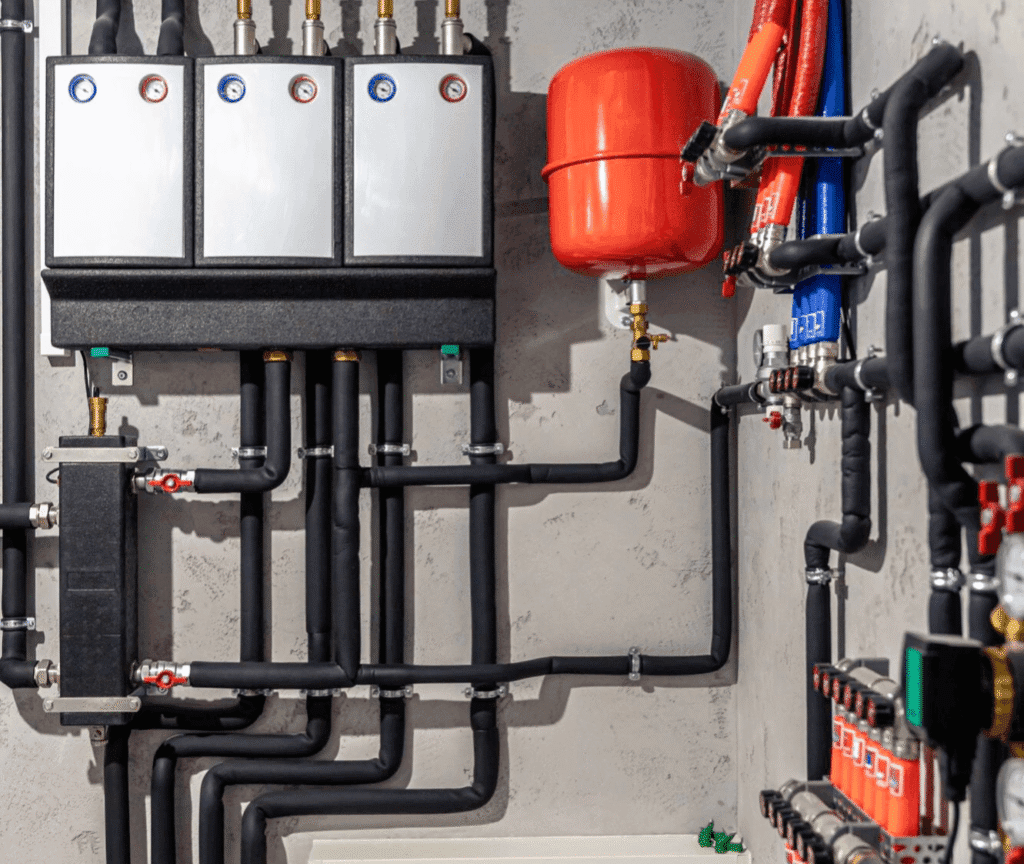
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Why Efficiency in Heat Air Systems Matters Energy Savings Efficiency in Heat Air
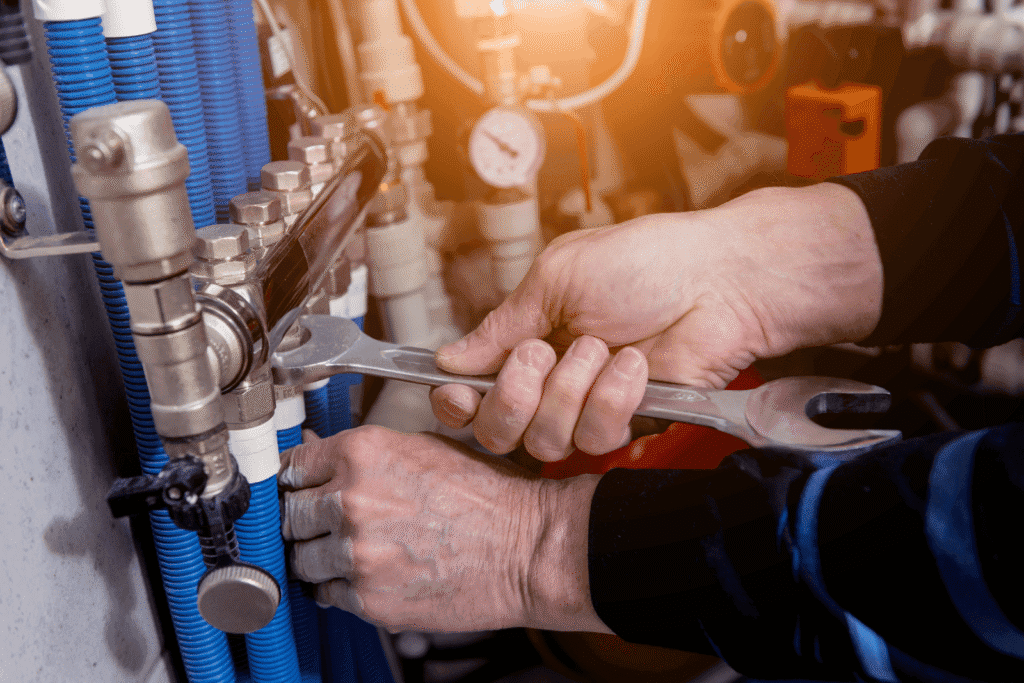
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: A furnace is the heart of your home’s heating system. Its heating element
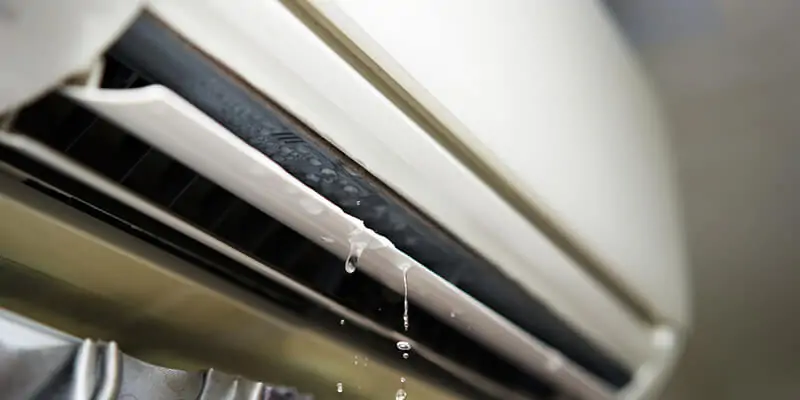

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Air conditioning is a lifesaver, especially during those scorching summer days. But what
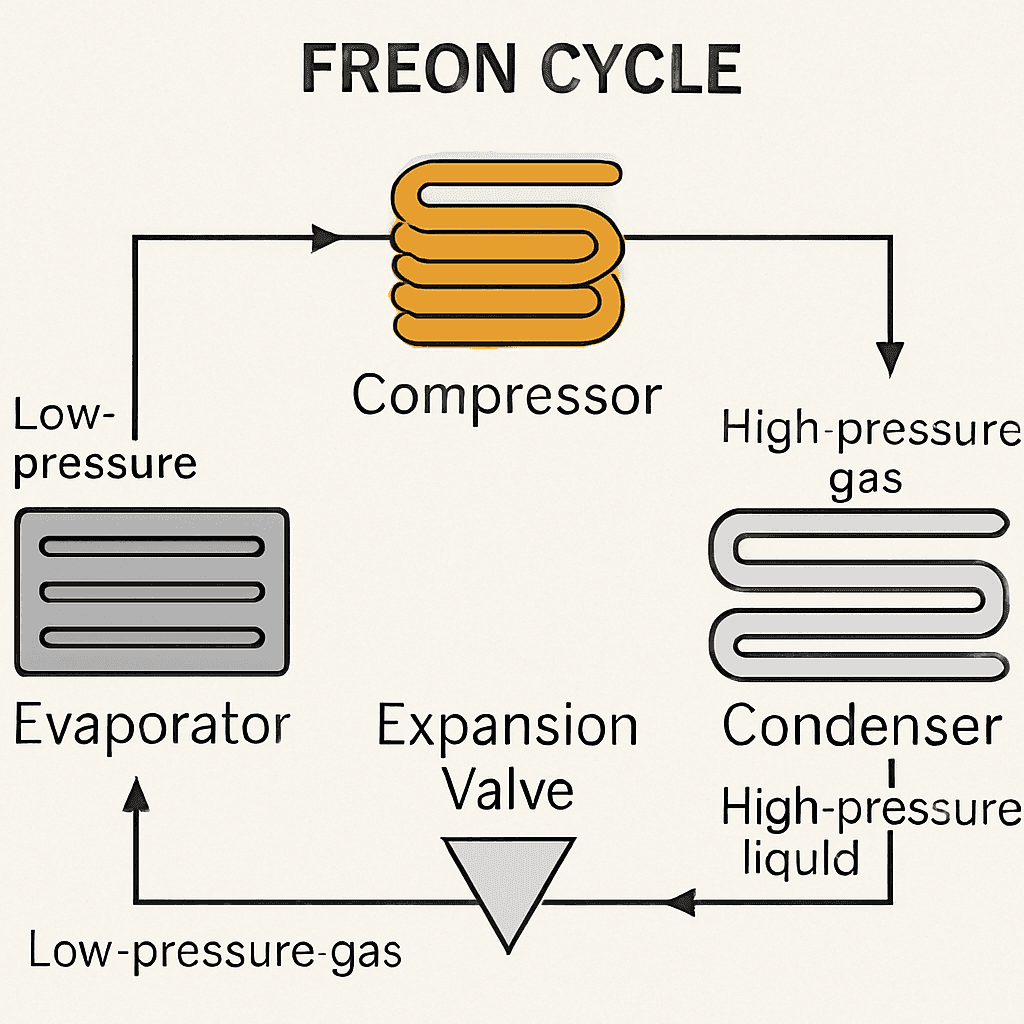
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Freon is a name you might have heard when discussing air conditioning. But

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Air conditioning is a lifesaver, especially during those scorching summer days. But what
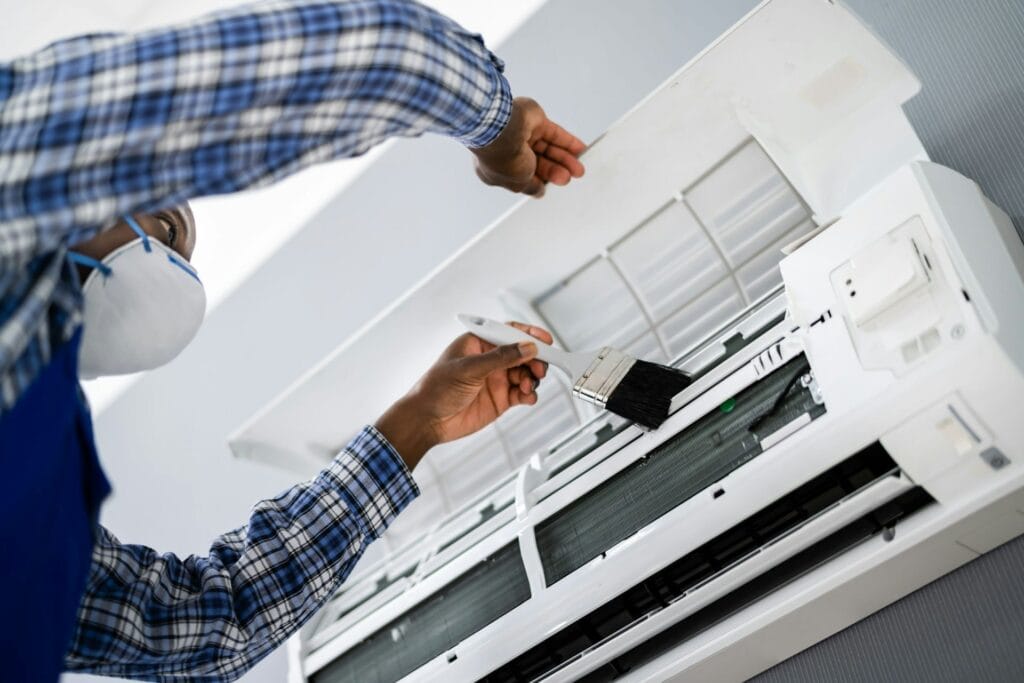

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Choosing AC Service is crucial for maintaining a comfortable home or business environment.

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: The Importance of Proper AC Ventilation Air conditioning is more than just cooling.
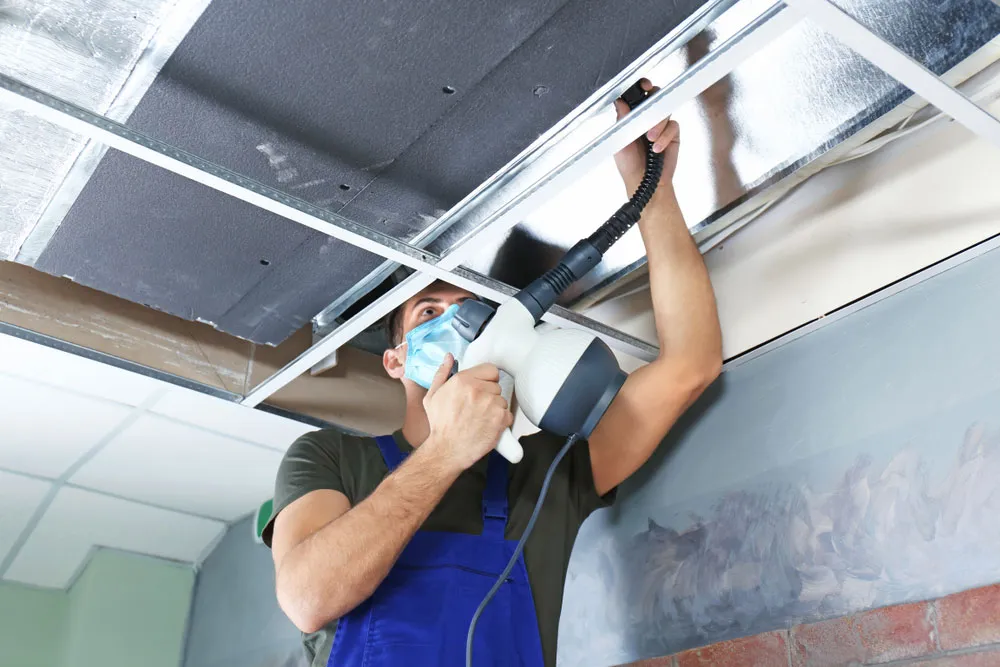

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Keeping your air vents clean is more important than you might think. It’s

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Why Your Thermostat Clicks but the AC Does Not Turn On In the

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: # Furnace Not Heating? Maintenance Tips for Furnace Heating Elements When the chill

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: In the heart of Hollywood, where the sun shines bright, a good air

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Building a new home is an exciting journey. It’s a chance to create

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Understanding the Importance of BTUs in Your HVAC System Understanding the intricacies of
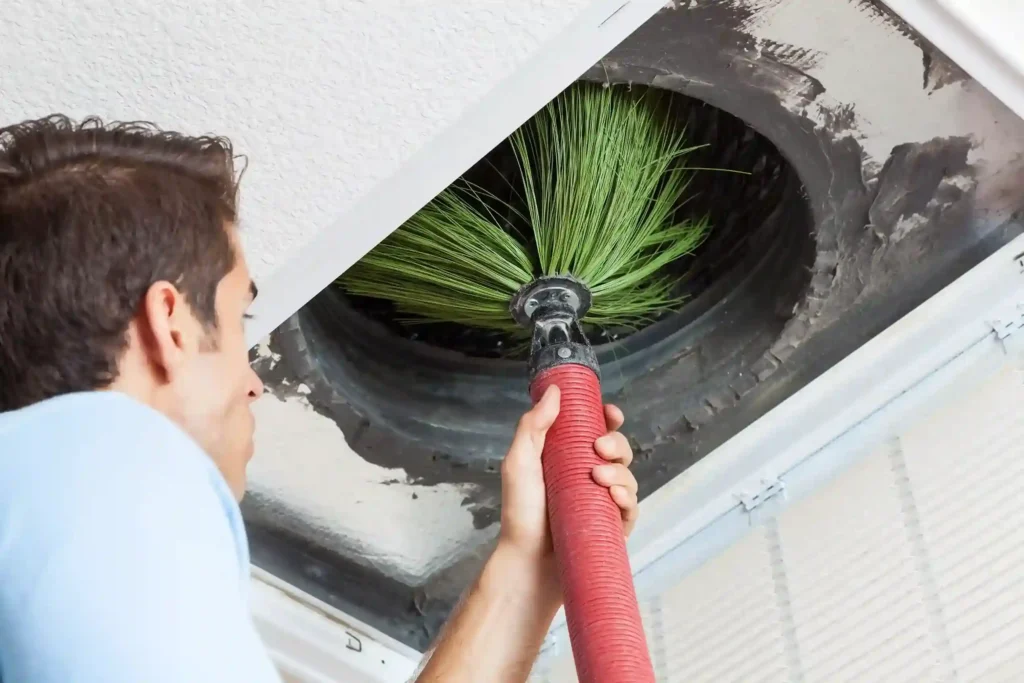

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: The Importance of Regular Duct Cleaning Services When it comes to maintaining a
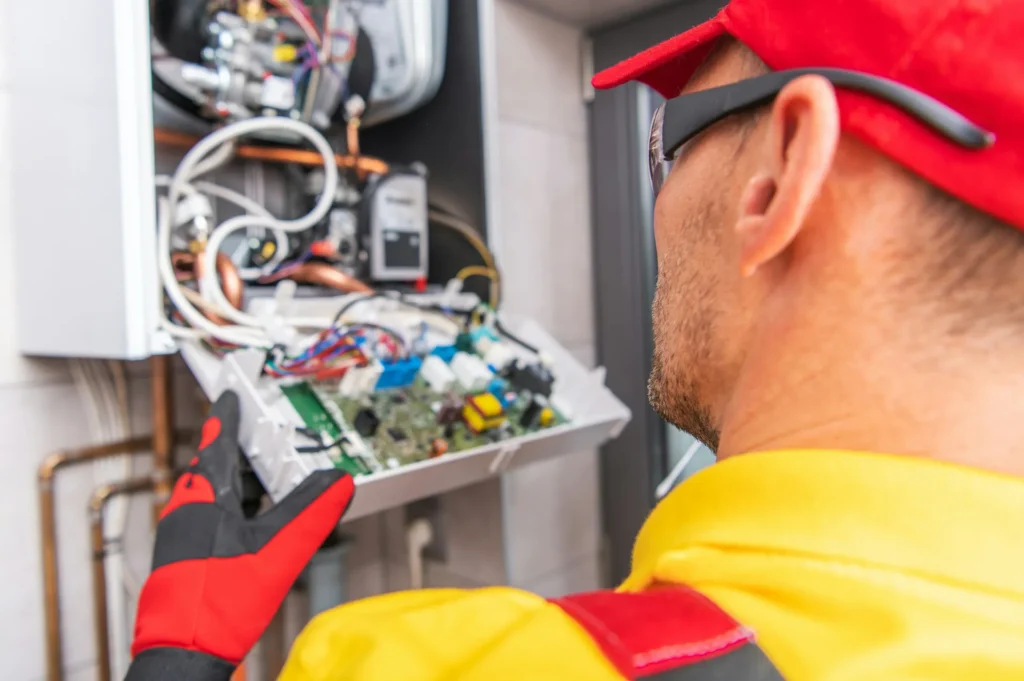

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Winter Humidity and Its Impact on Furnace Efficiency Winter brings a chill in
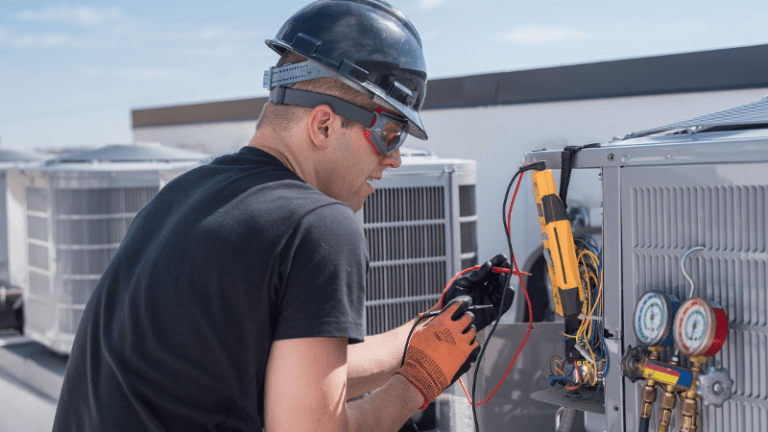

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Why an HVAC Disconnect Switch Is Essential for Safety When it comes to
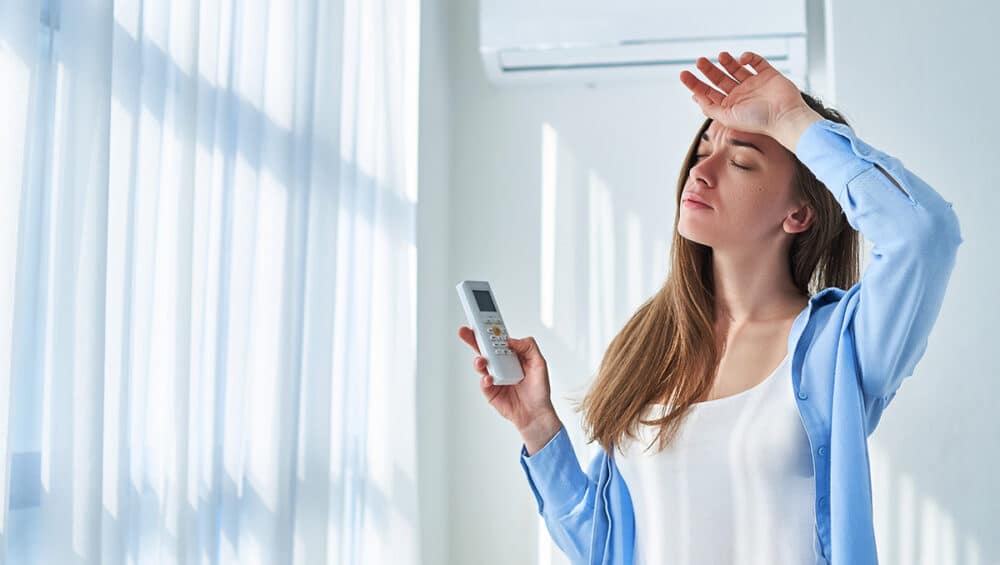

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: As the owner of LC Heating and Air Conditioning in Hollywood, I understand

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Los Angeles is known for its vibrant culture and sunny weather. But there’s

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Why Your Heater Blows Cold Air: Causes and Solutions When your heater starts

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Choosing the right HVAC system is crucial for comfort and efficiency. With so

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Deciding between repairing or replacing your HVAC heater furnace can be daunting. It’s
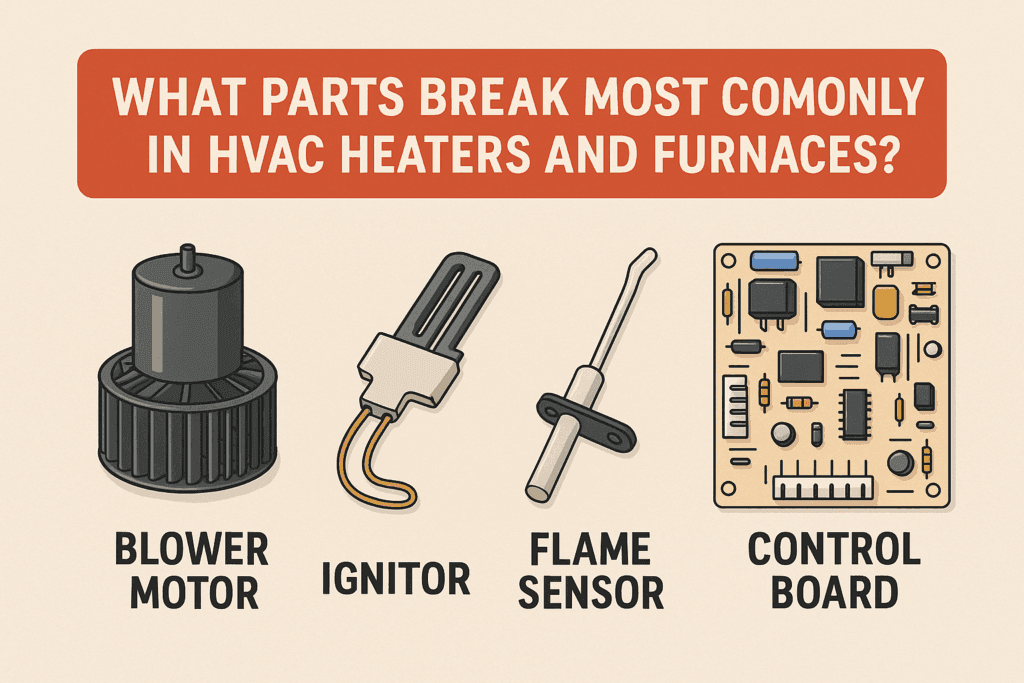
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: When the chill of winter sets in, a reliable heater is a must.

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Asbestos ductwork in Pasadena homes is a hidden danger many homeowners may not
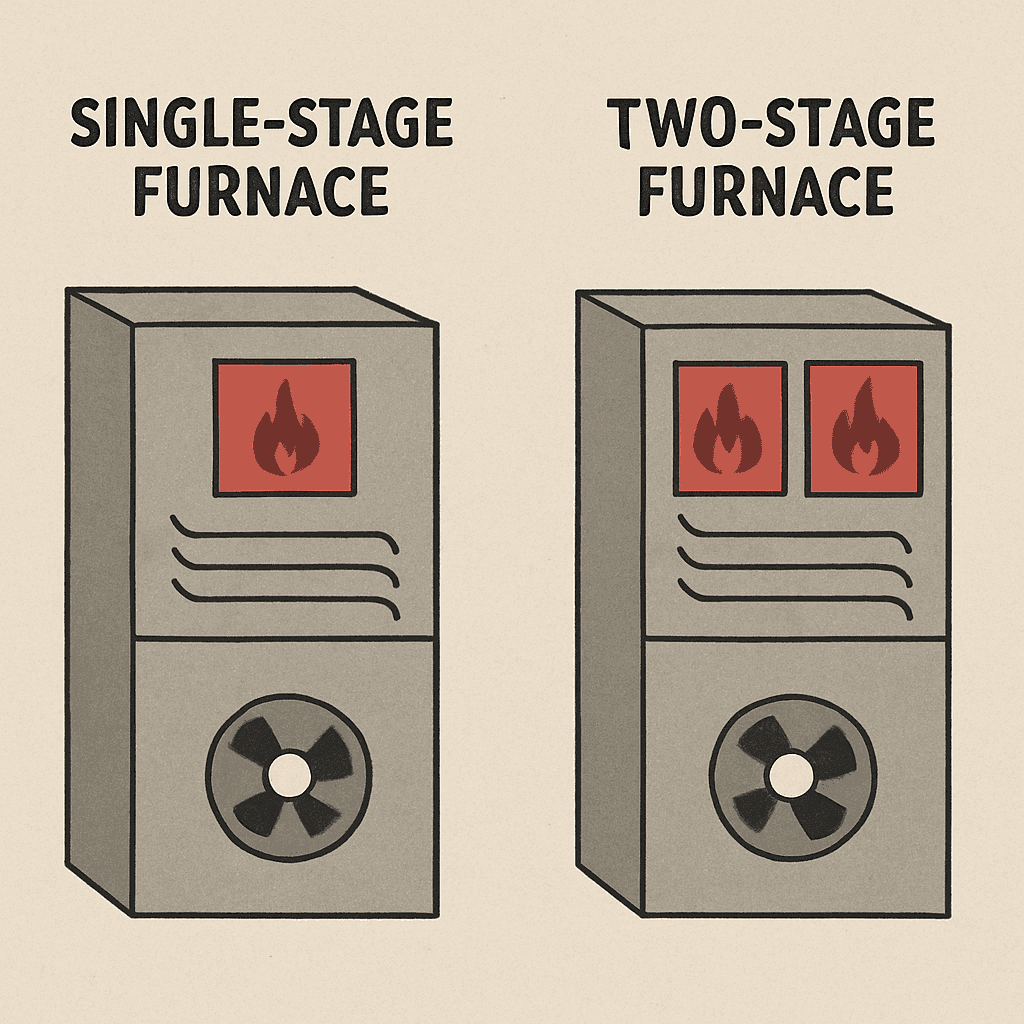
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Choosing the right furnace for your home is crucial. It impacts comfort, energy

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Winter in Los Angeles might not be as harsh as in other places,
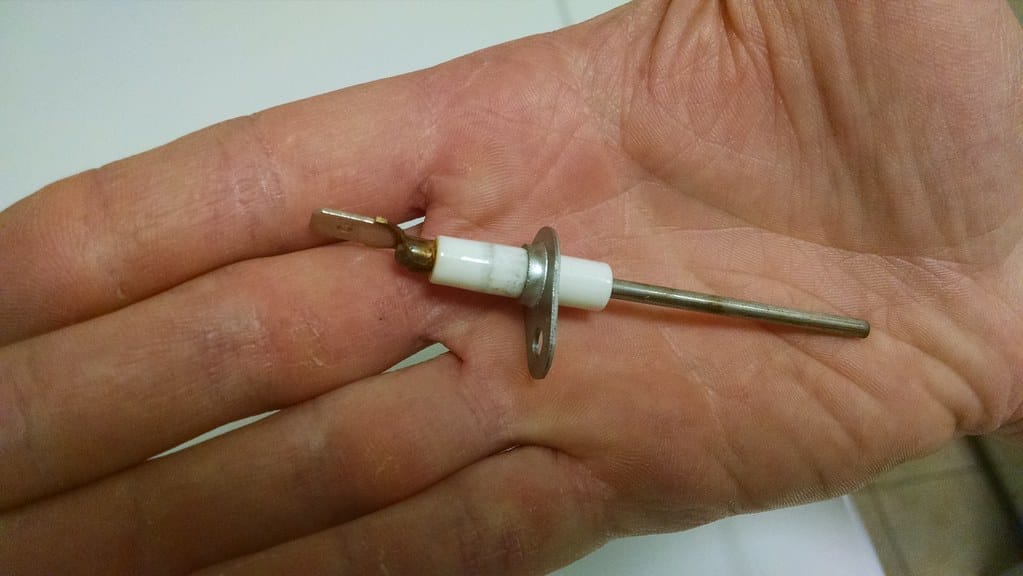

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Is your heater blowing cold air when it should be warming your home?
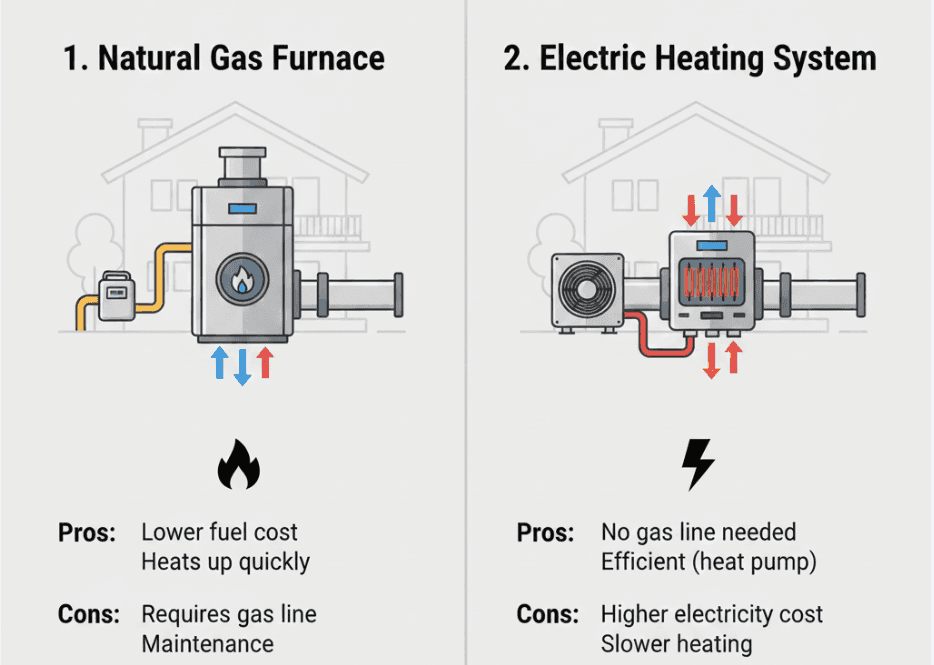
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Choosing the right heating system for your home or business is crucial. It
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Heating solutions vary widely in their mechanics, energy efficiency, and installation requirements. Whether

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: As a trusted provider of HVAC services in Hollywood, I understand that maintaining
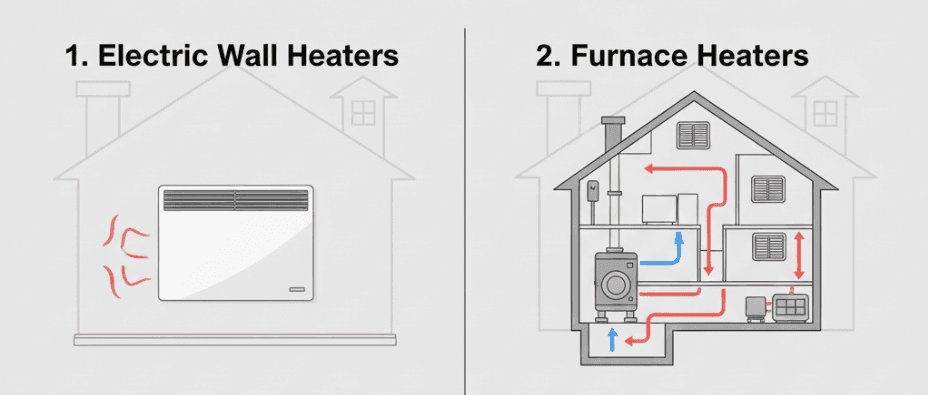
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: In the hustle and bustle of our daily lives, it’s easy to overlook

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: As the chill of winter sets in, a reliable furnace becomes essential. But
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Weather forecasts play a crucial role in our daily lives, especially for those

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: When your heater starts blowing cold air, it can be frustrating and uncomfortable.

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: When the chill of winter sets in, a reliable furnace is essential. But
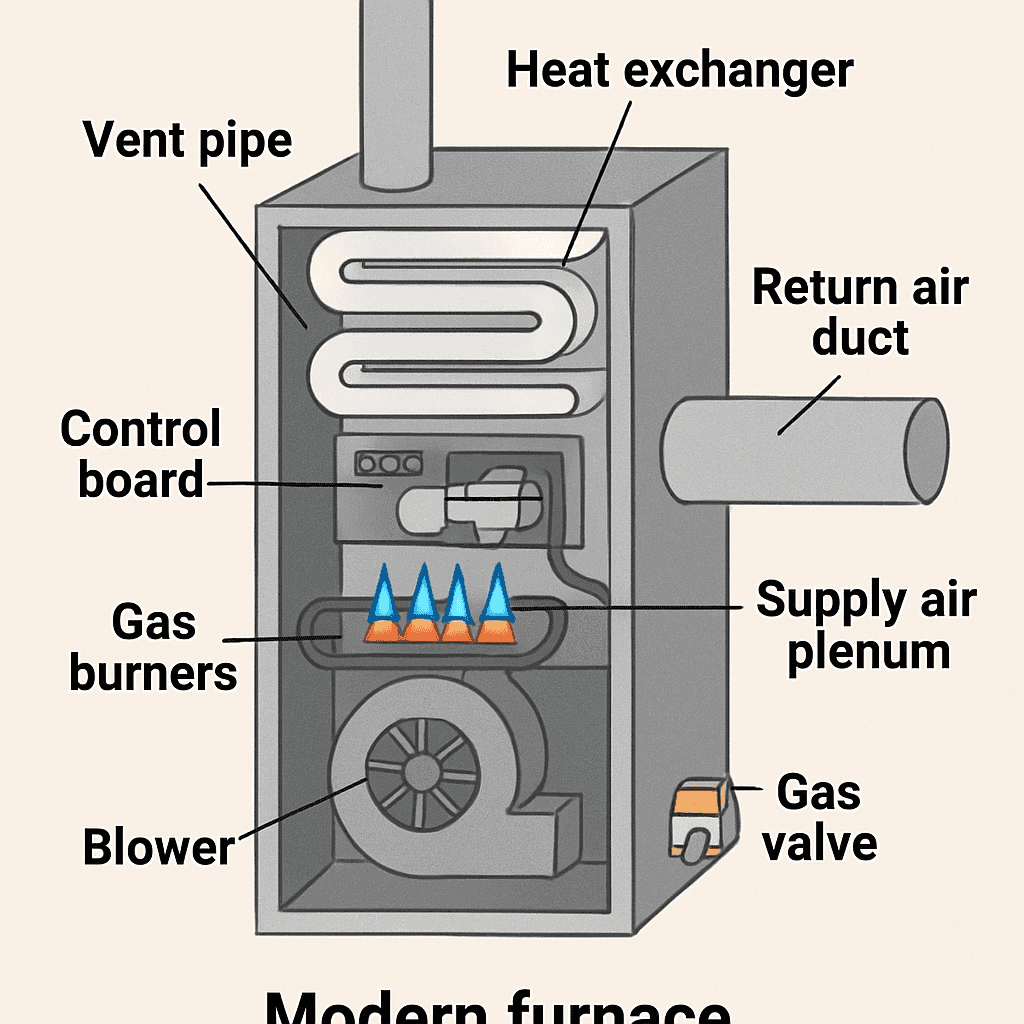
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: In today’s fast-paced world, comfort at home is more important than ever. A
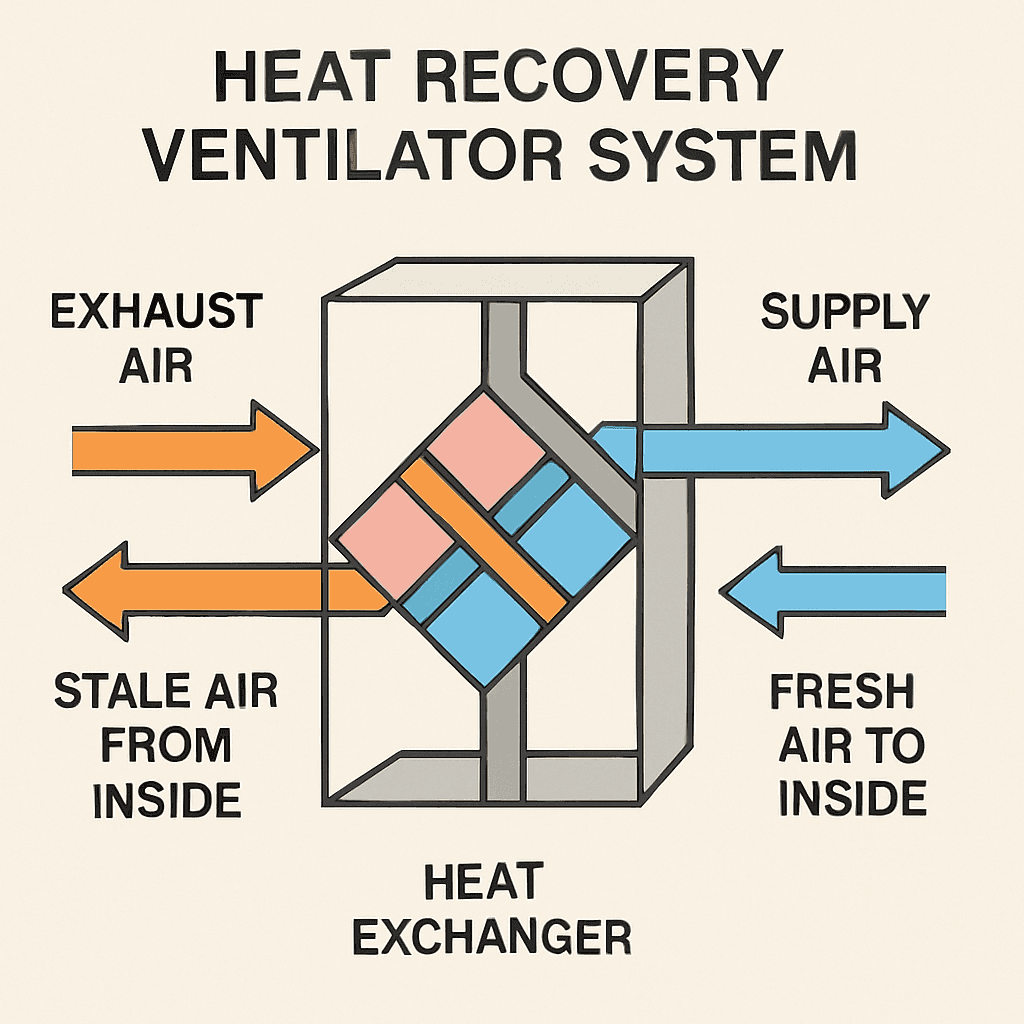
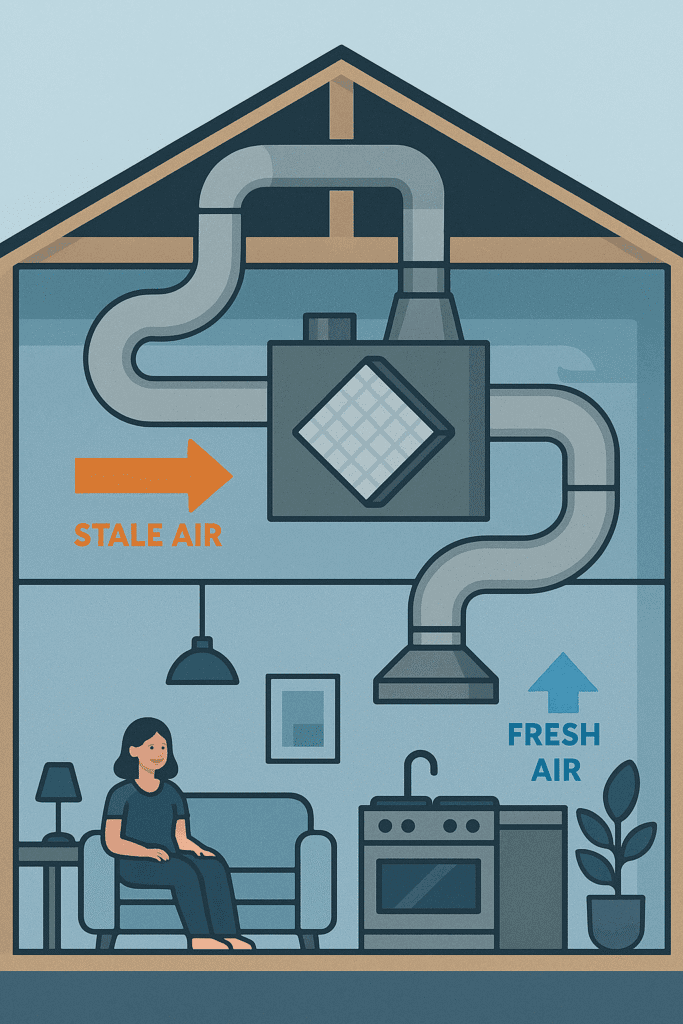
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: In today’s world, maintaining a healthy home environment is crucial. Indoor air quality plays a significant role in our well-being. Many homeowners are turning to Heat Recovery Ventilators (HRVs) for a solution. HRVs are designed to improve air quality by exchanging stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air. They do this while recovering heat from the outgoing air. This process not only enhances air quality but also reduces energy costs. For homes that are tightly sealed, HRVs are particularly beneficial. They ensure a consistent flow of fresh air, which is essential for comfort and health. By maintaining a steady indoor temperature, HRVs enhance overall comfort. Moreover, HRVs help reduce humidity levels. This prevents mold growth and improves air quality. They are different from Energy Recovery Ventilators (ERVs), which also manage humidity by transferring moisture. Understanding how HRVs work can empower homeowners. It allows them to make informed decisions about their ventilation needs. In this article, we’ll explore how HRVs optimize home ventilation systems and energy bills. What Is a Heat Recovery Ventilator (HRV)? A Heat Recovery Ventilator (HRV) is an essential component for modern home ventilation. This device continuously replaces stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air. The brilliance of an HRV lies in its ability to reclaim heat from outgoing air. Think of an HRV as a smart airflow manager. It uses a heat exchanger to transfer warmth from indoor air to incoming air. This results in less energy needed to heat or cool the home. Here are some key aspects of an HRV: An HRV is advantageous for tightly sealed homes. It compensates for the lack of natural ventilation and ensures a consistent indoor climate. This consistent exchange of air contributes to improved indoor air quality. Overall, an HRV is more than just a fan—it is an investment in your home’s air quality. By reducing the energy needed to maintain comfort, it also saves on utility bills, making it a valuable addition to any home. How Does Heat Recovery Work? Understanding how heat recovery works can empower homeowners. An HRV system is designed to maximize efficiency by transferring heat between outgoing and incoming air. This process helps maintain a comfortable indoor climate without over-relying on your HVAC system.
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Choosing the right 2 Ton AC for your home is crucial to ensuring

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: As temperatures rise during the sweltering summer months, ensuring your home remains a

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Choosing the right air conditioner for your home can be daunting. With so
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Packaged HVAC systems are a smart choice for many homeowners. They combine heating

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Choosing between Professional vs. DIY Mini Split Costs can be daunting. Each option

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Tackling a DIY mini split project can be both exciting and daunting. Many
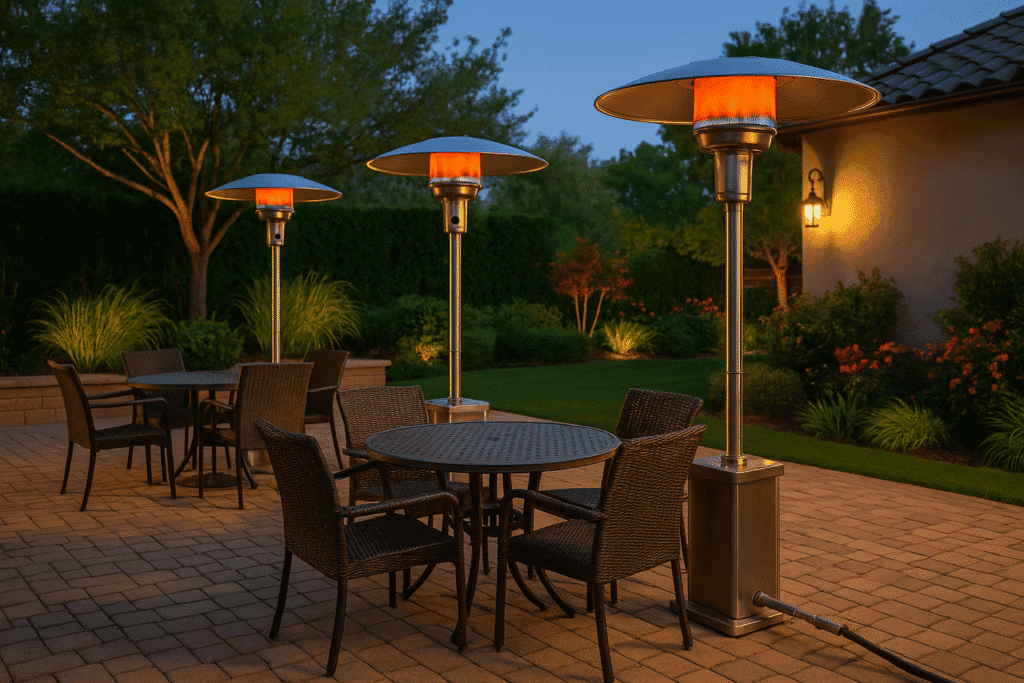
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Natural gas patio heaters are a popular choice for outdoor comfort in Pasadena.
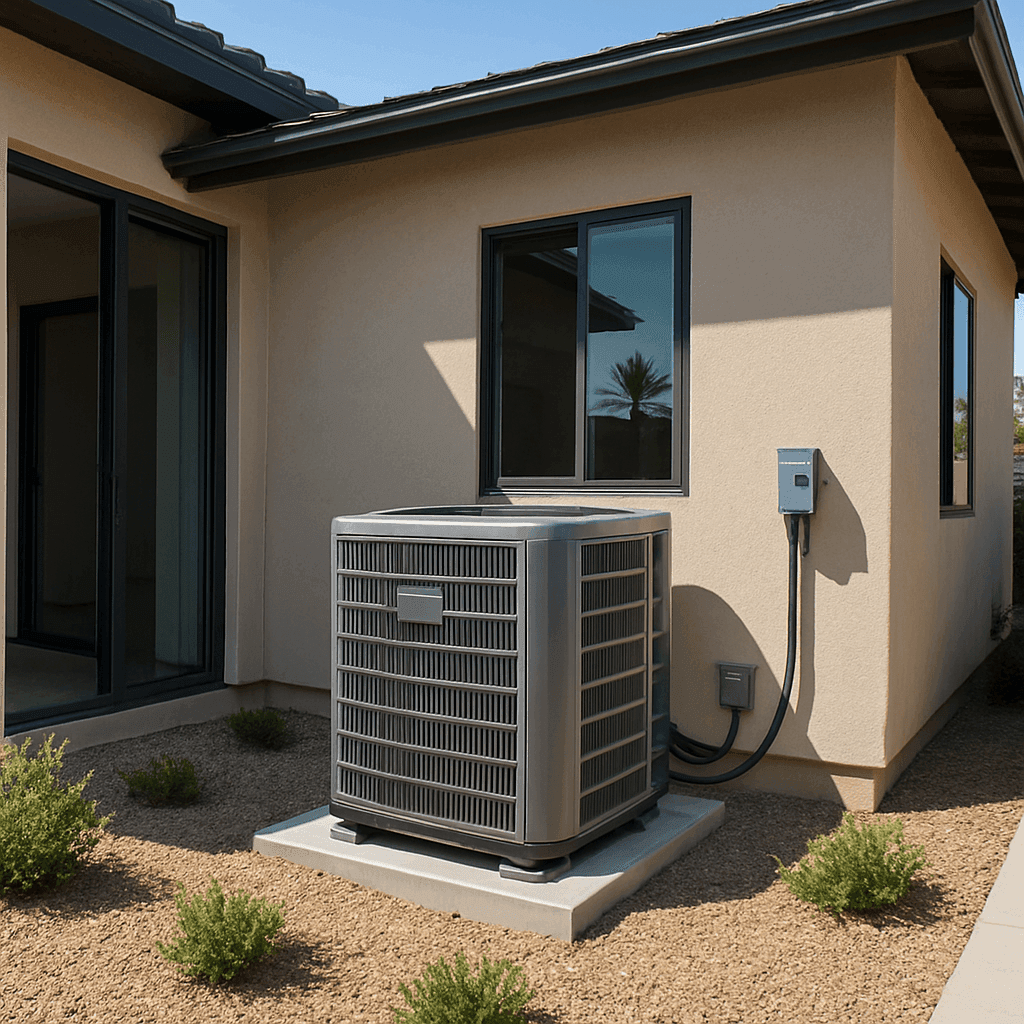
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: California homeowners often face a tough decision: HVAC Repair or replacement. This choice
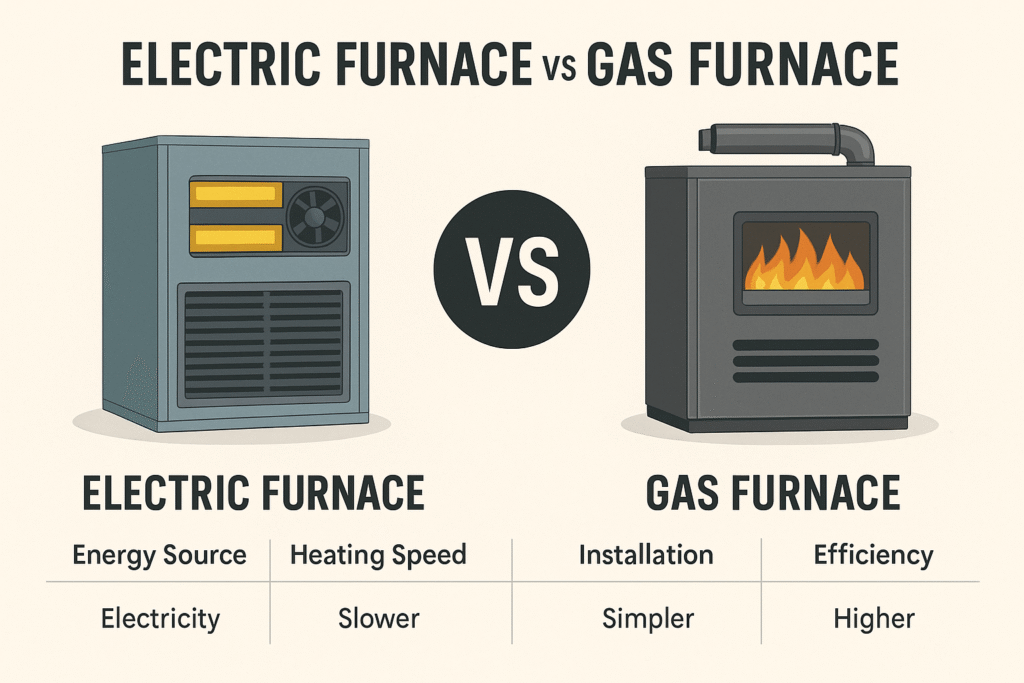
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: When it comes to choosing the right furnace for your home in Los
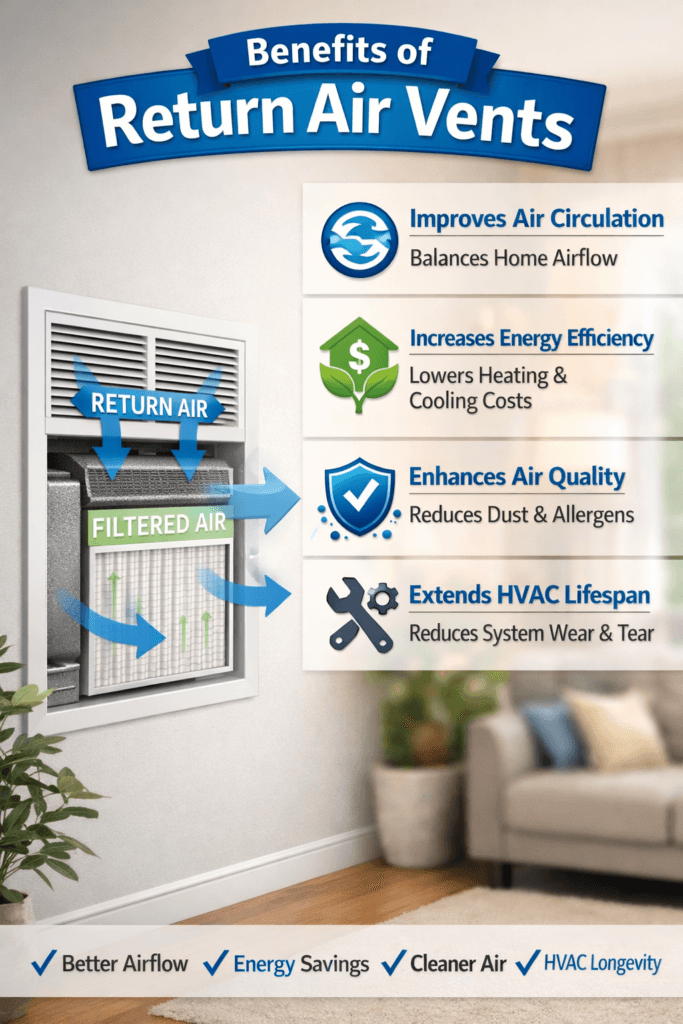
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Benefits of Return Air Vents are often overlooked, but they play a crucial
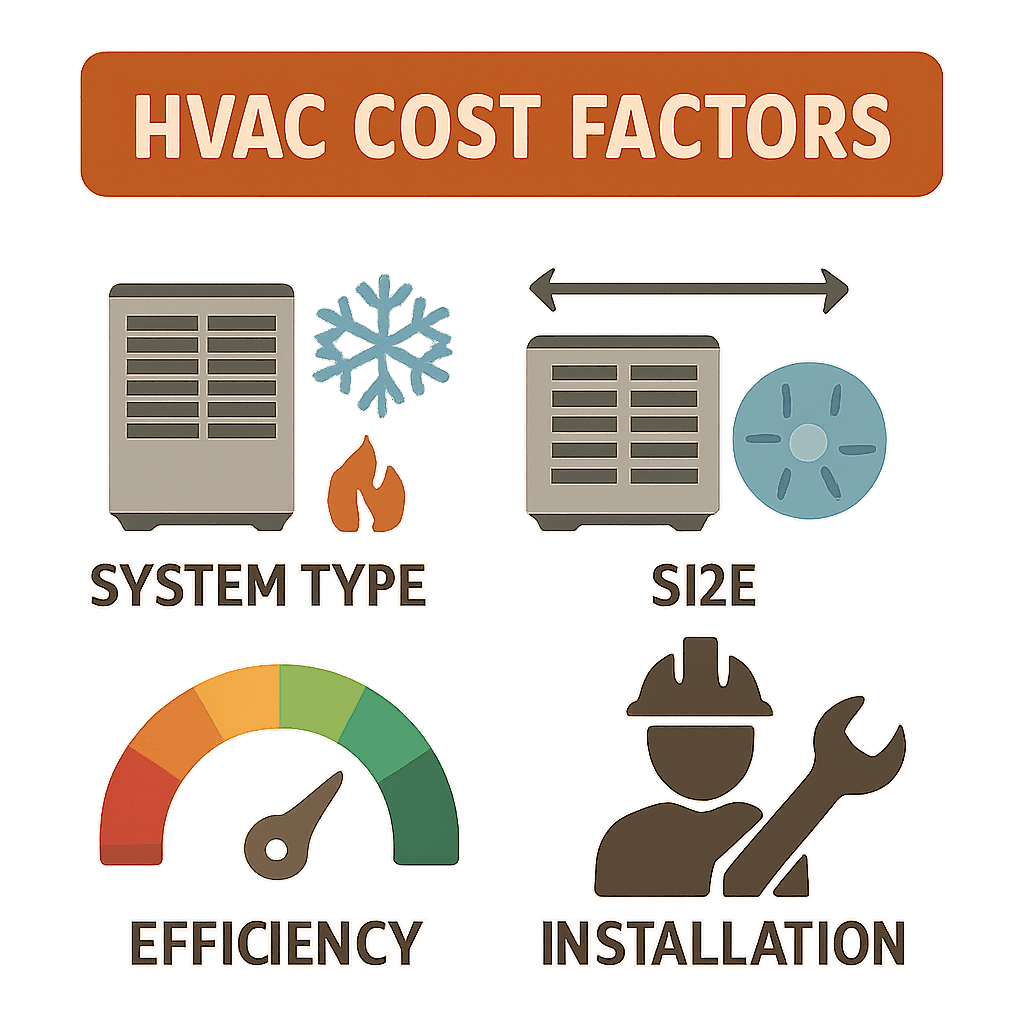
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Hello neighbors! From our family here at LC Heating and Air on Fairfax
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: When it comes to maintaining a comfortable and healthy home environment, indoor air
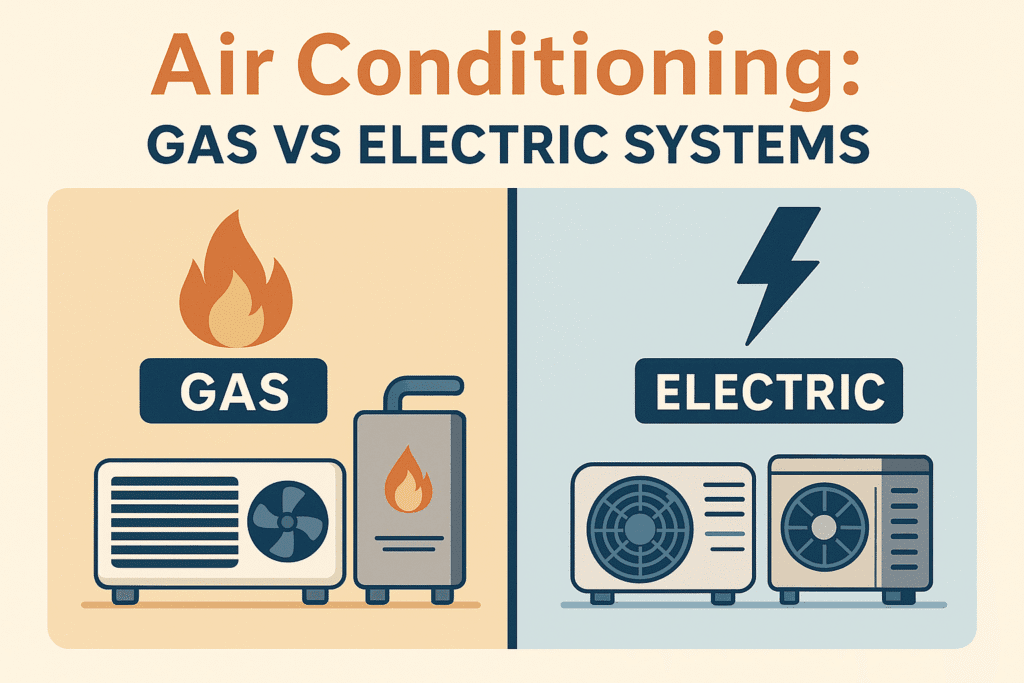
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Whether you’re a busy stay-at-home mom, a small business owner, or a work-from-home
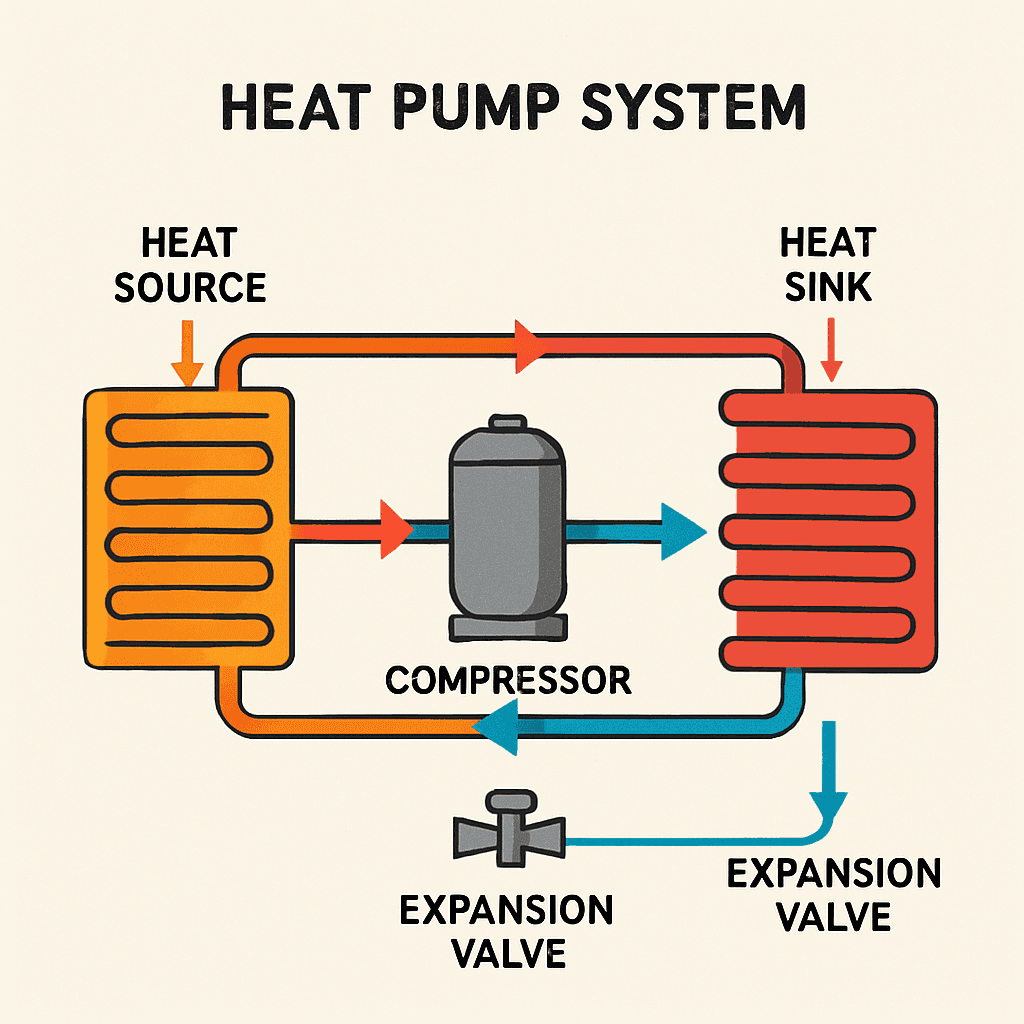
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: What Is a Heat Pump? Understanding How Heat Pumps Work is key to
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: When it comes to maintaining a comfortable home environment, air handlers play a
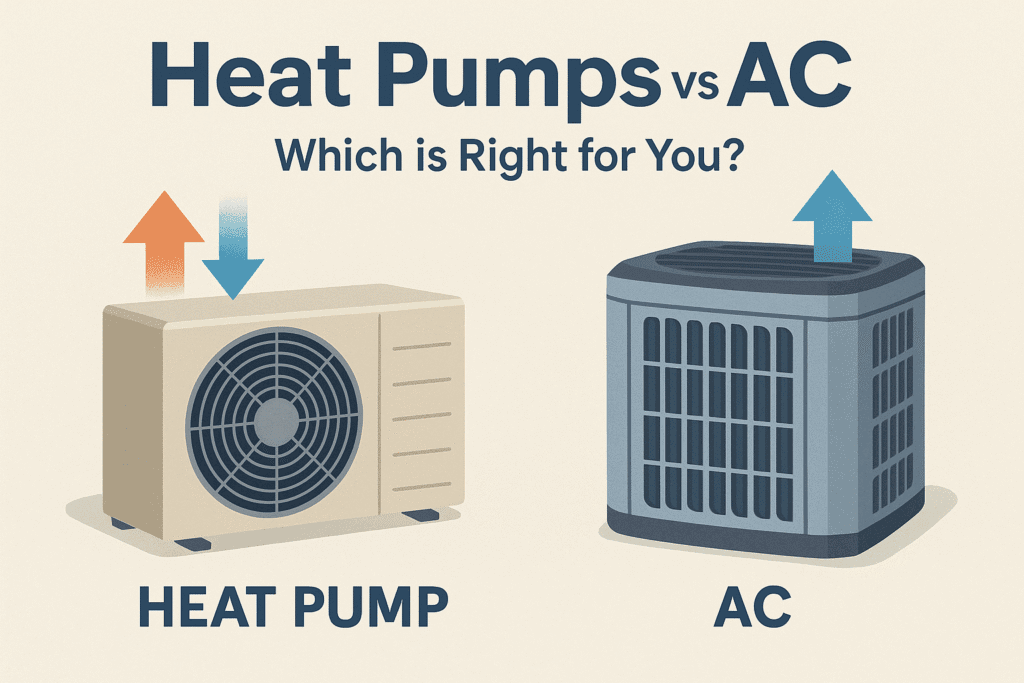
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Selecting the right heating and cooling solution for your home can be quite

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: No Power to Thermostat Issues can be frustrating, especially when your thermostat loses
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Securing Appliance Rebates is crucial not only for immediate financial savings but also
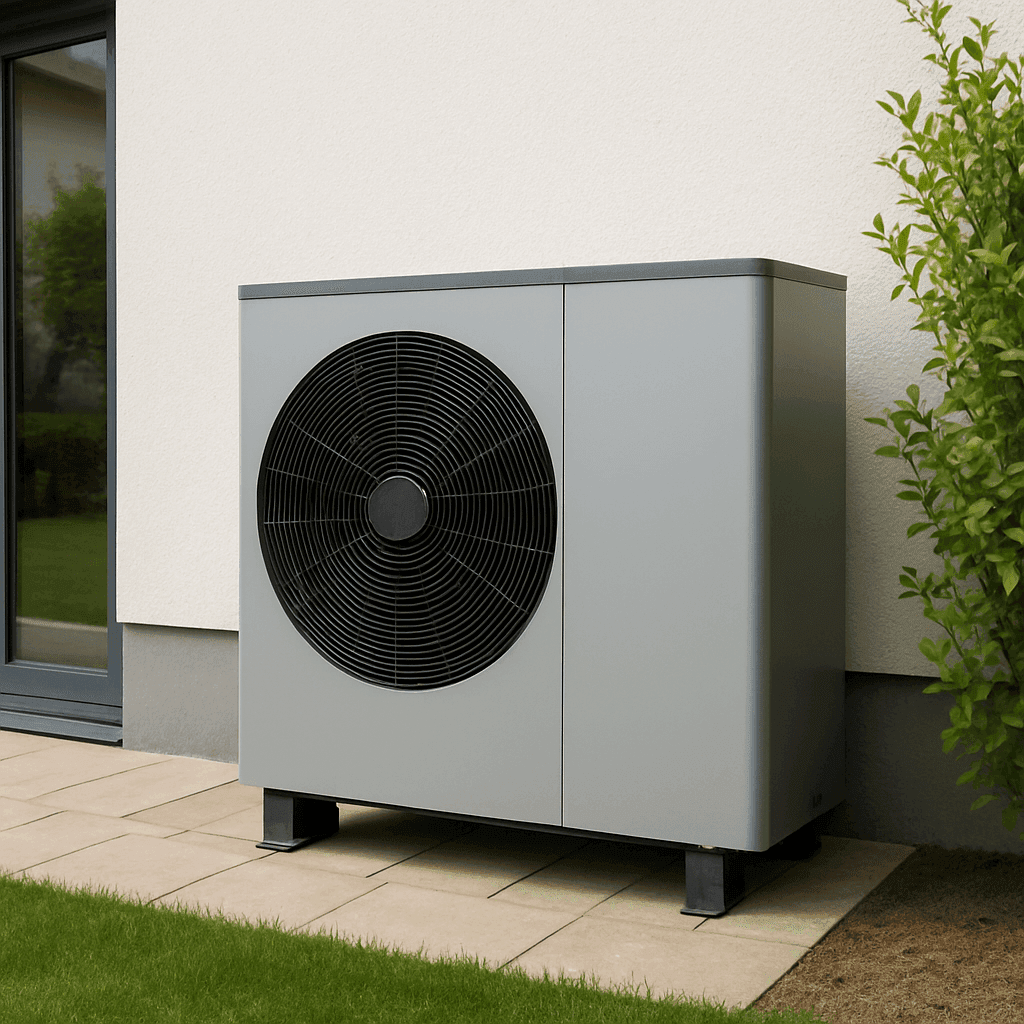
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Heat Pumps Improve Home Efficiency by offering an energy-saving solution for both heating
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: As the temperatures begin to dip in Los Angeles, ensuring your home remains

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Heehra is more than just a word; it’s a concept rich with cultural
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Before diving into the specific factors influencing the Furnace Replacement Price, it’s essential
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Navigating the world of energy tax credit California can be daunting, but it
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Typically, a well-maintained furnace can last between 15 to 20 years. However, as
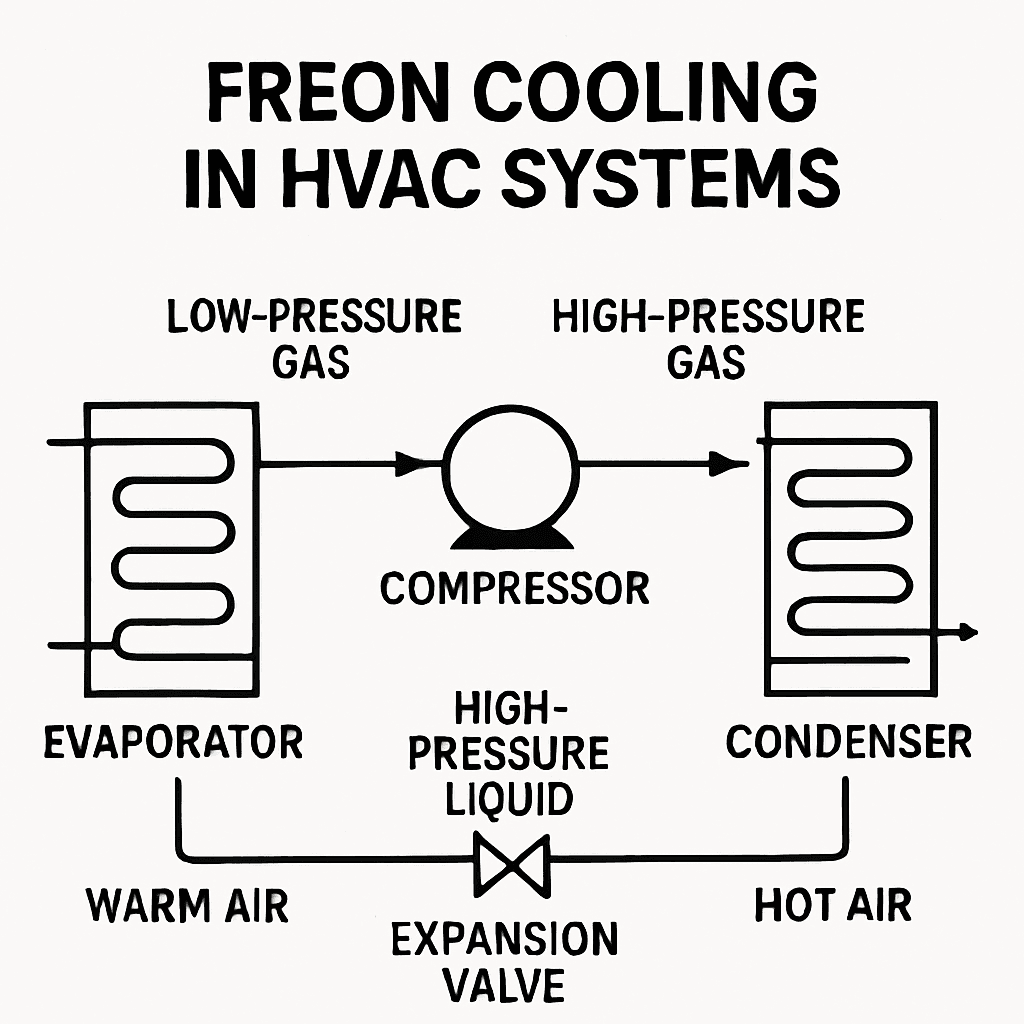
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Freon is a name you might have heard, especially if you own an

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Before diving into the solutions, it’s essential to understand what causes AC leaks.
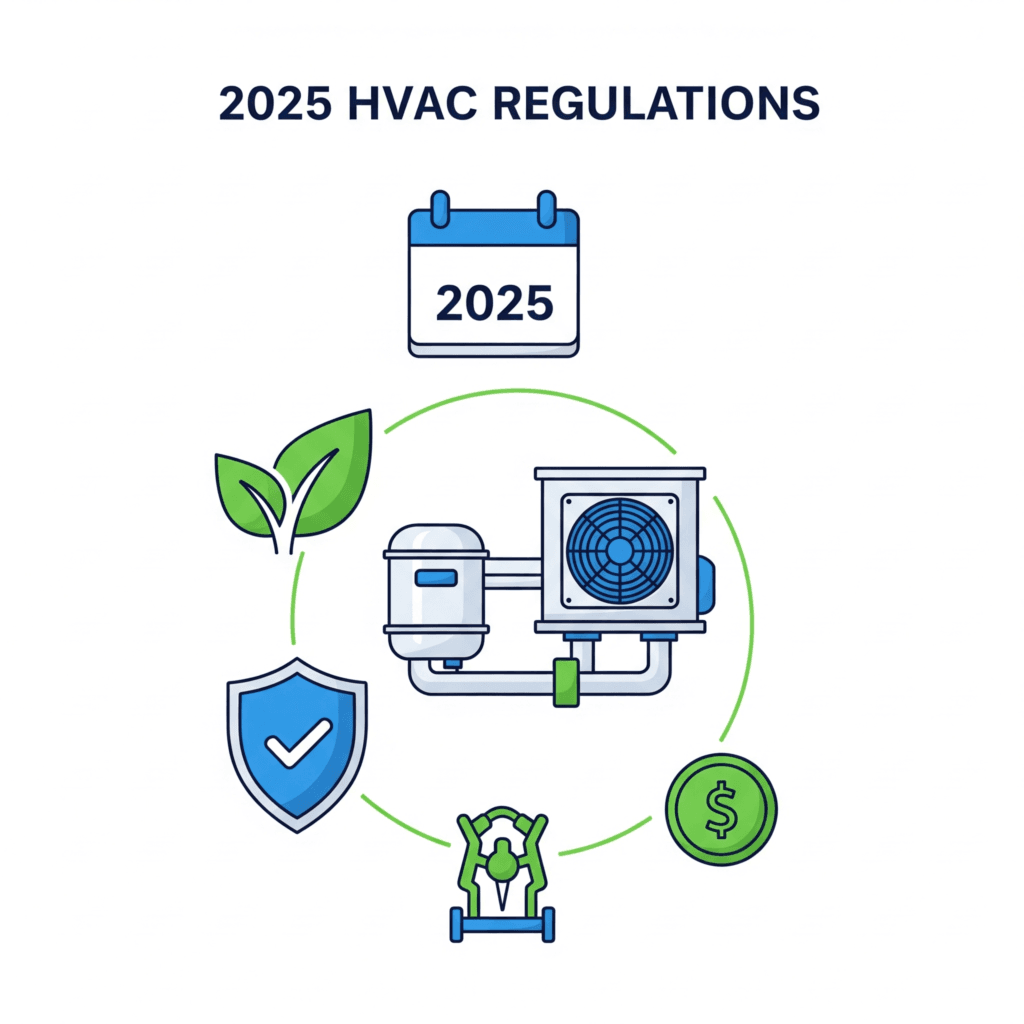
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: The world of HVAC is about to change. The 2025 HVAC regulations are

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Air conditioning is a lifesaver during hot summer days. But what happens when
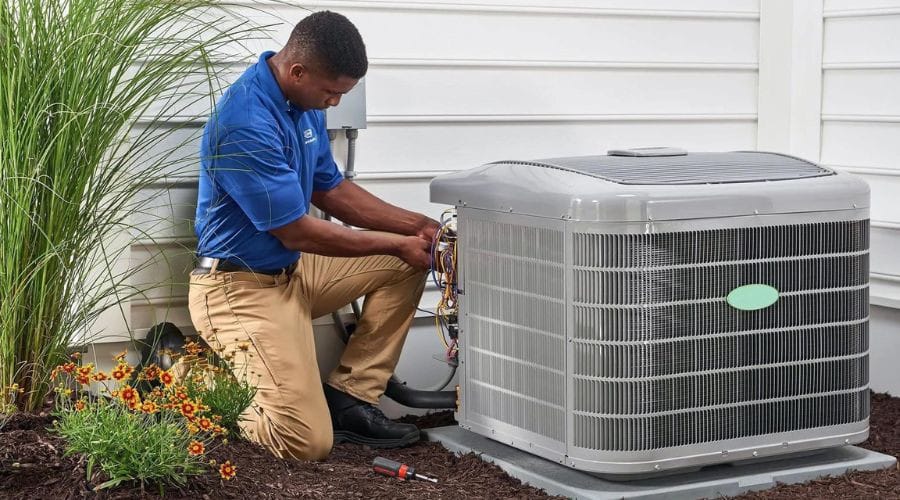

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: When your air conditioning unit starts to falter, deciding whether to repair or
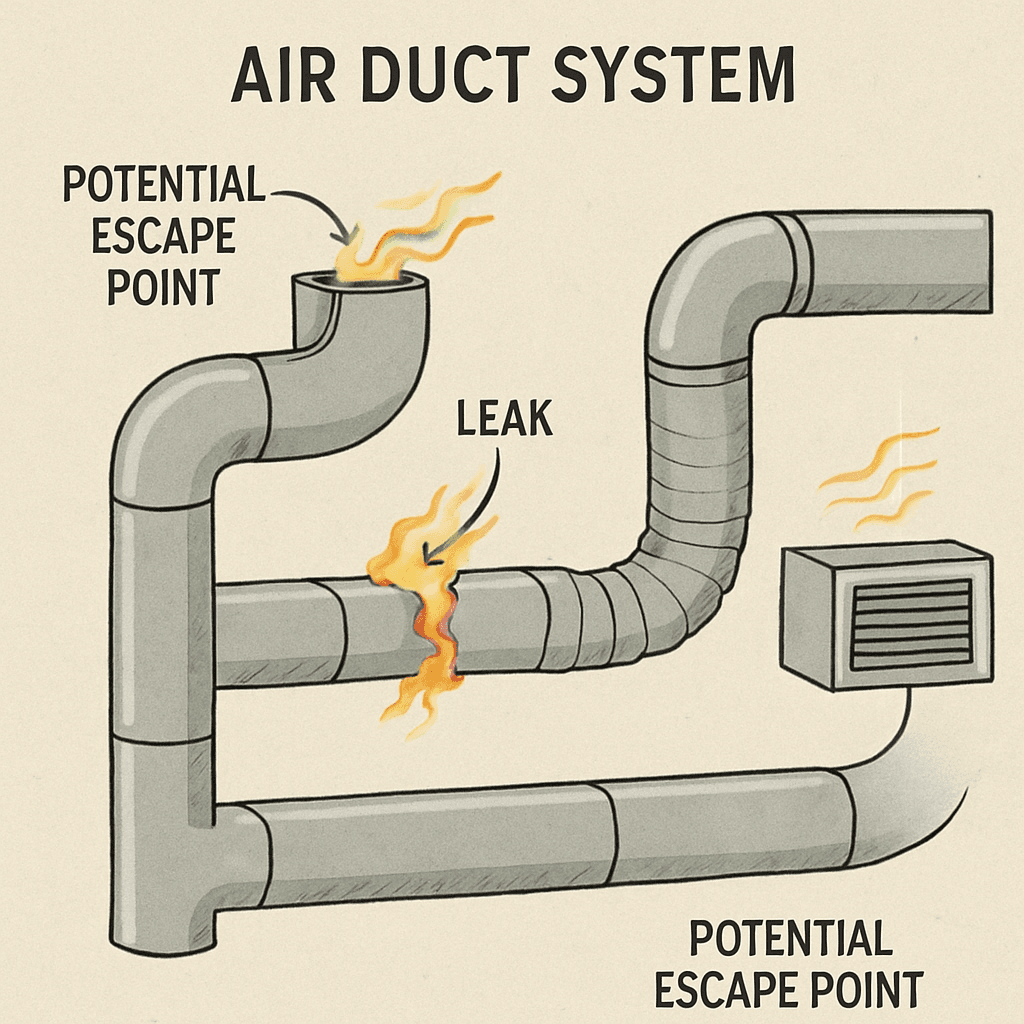
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Leaky air ducts can be a hidden culprit behind rising energy bills and
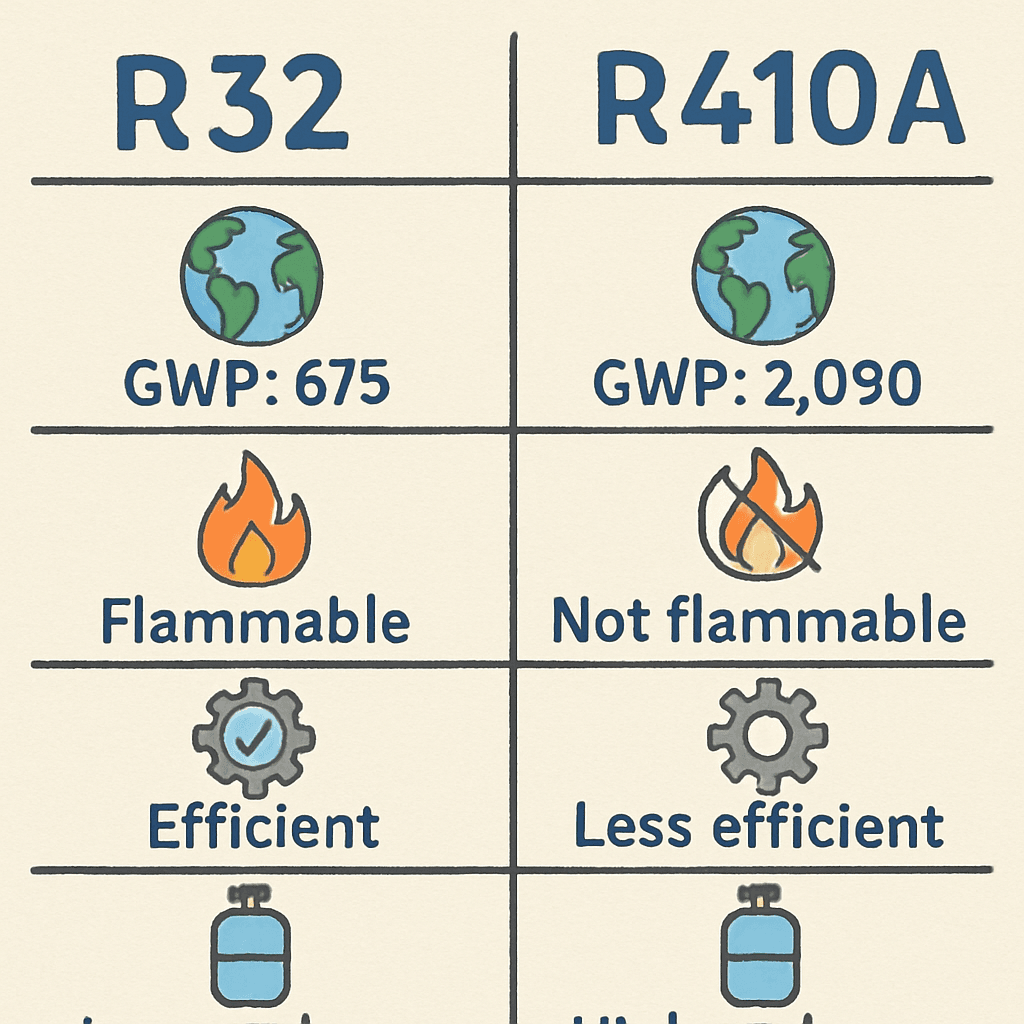
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: The 2025 refrigerant mandate is part of a global effort to reduce the
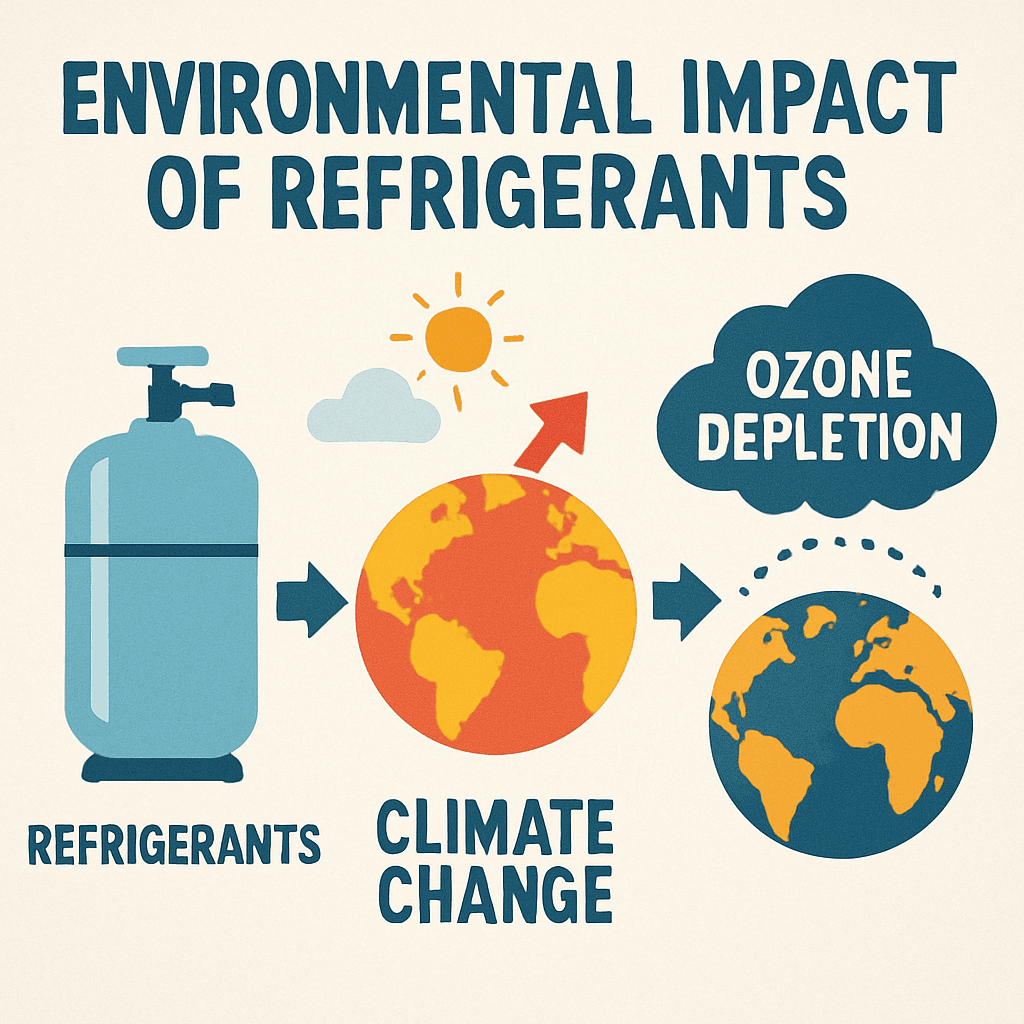
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: When it comes to modern air conditioning systems, understanding the differences between refrigerants

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: In the world of HVAC, dealing with leaks in air conditioning systems can
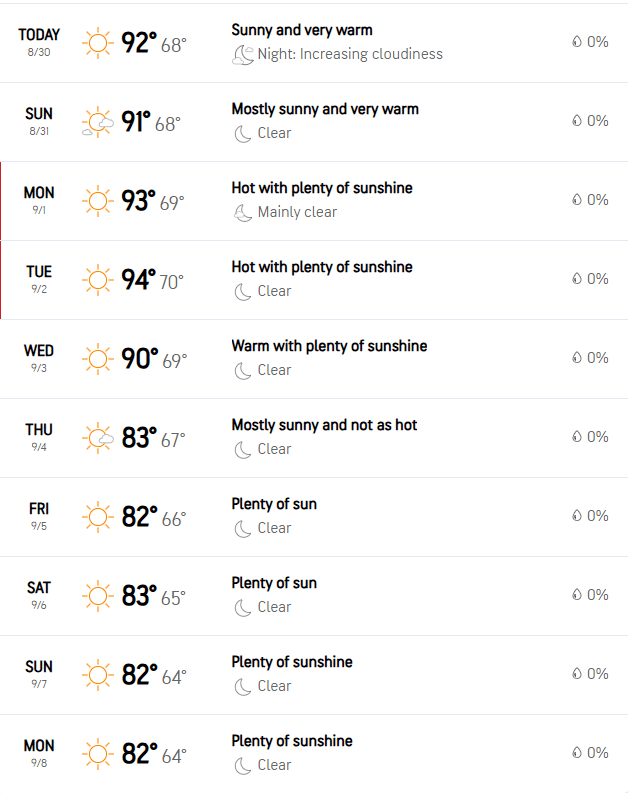
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: The upcoming Hollywood CA Labor Day Week Weather Forecast brings classic late-summer heat

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Falling asleep quickly can feel like a distant dream for many. Yet, a

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: In the hustle and bustle of modern life, a good night’s sleep can

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: As we step into September, the summer heat in Los Angeles begins to
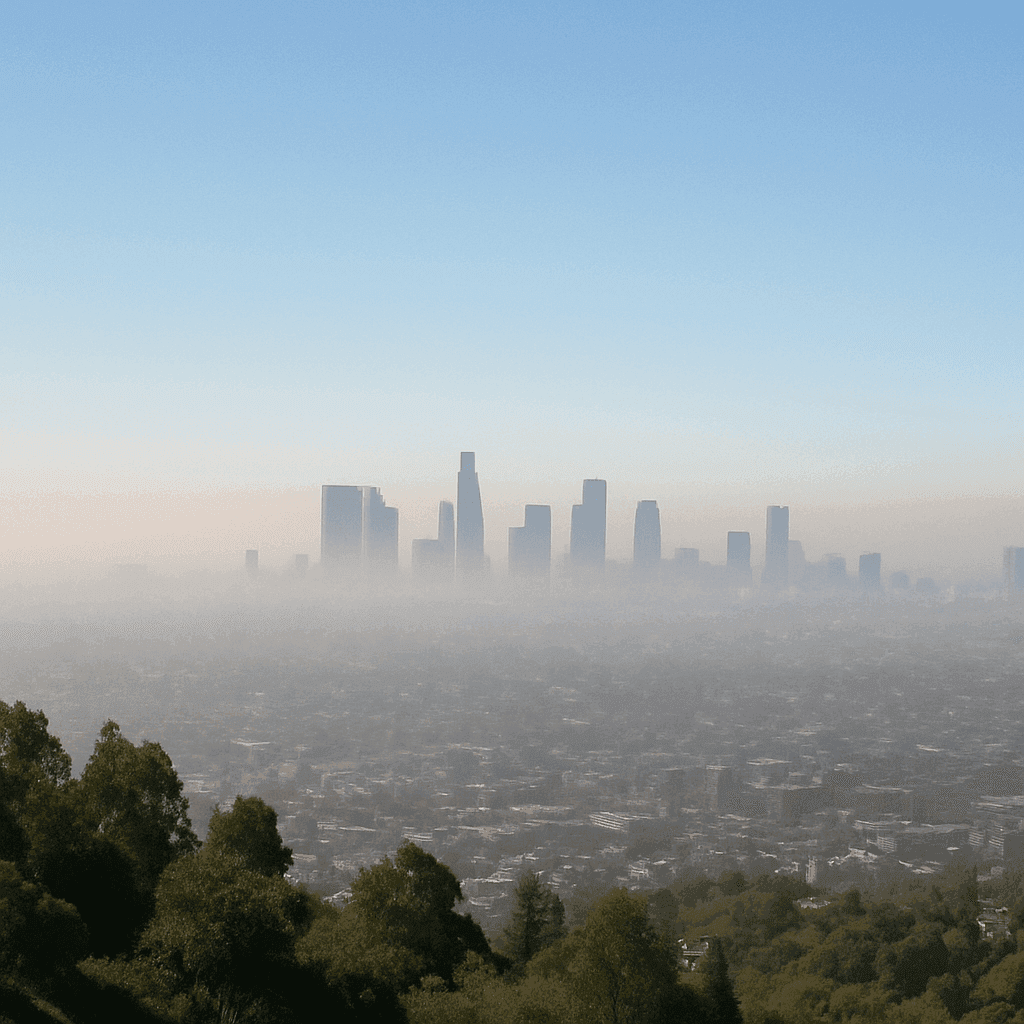

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Los Angeles is known for its vibrant culture and sunny skies. Yet, it
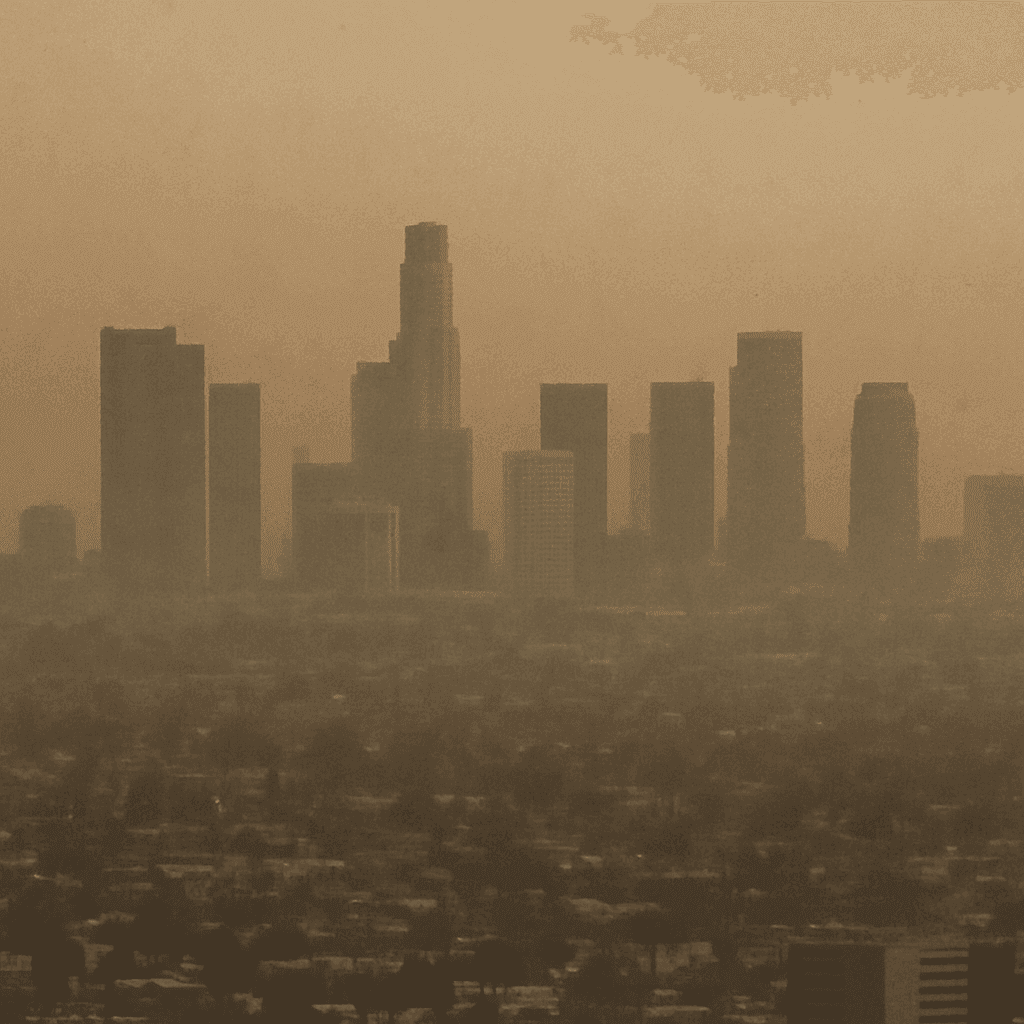

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Breathing clean air is essential for a healthy life. In Los Angeles, where
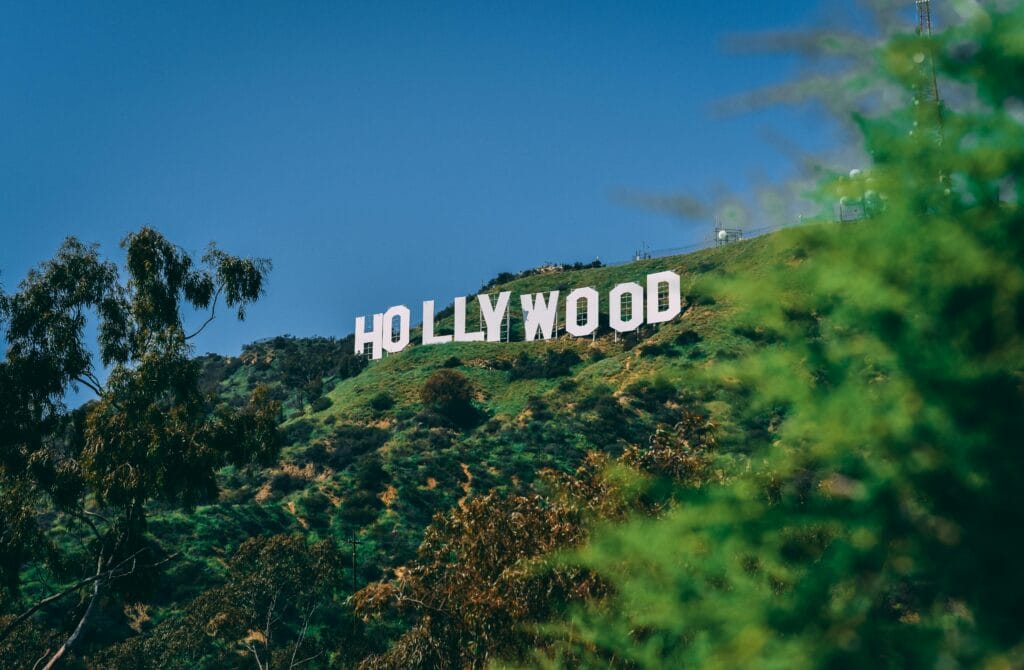

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Looking for the latest Hollywood CA weather forecast? You’re in luck—this week brings

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Los Angeles is known for its vibrant culture and sunny weather. But there’s
TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Maintaining your HVAC system is crucial for a healthy living environment and optimal
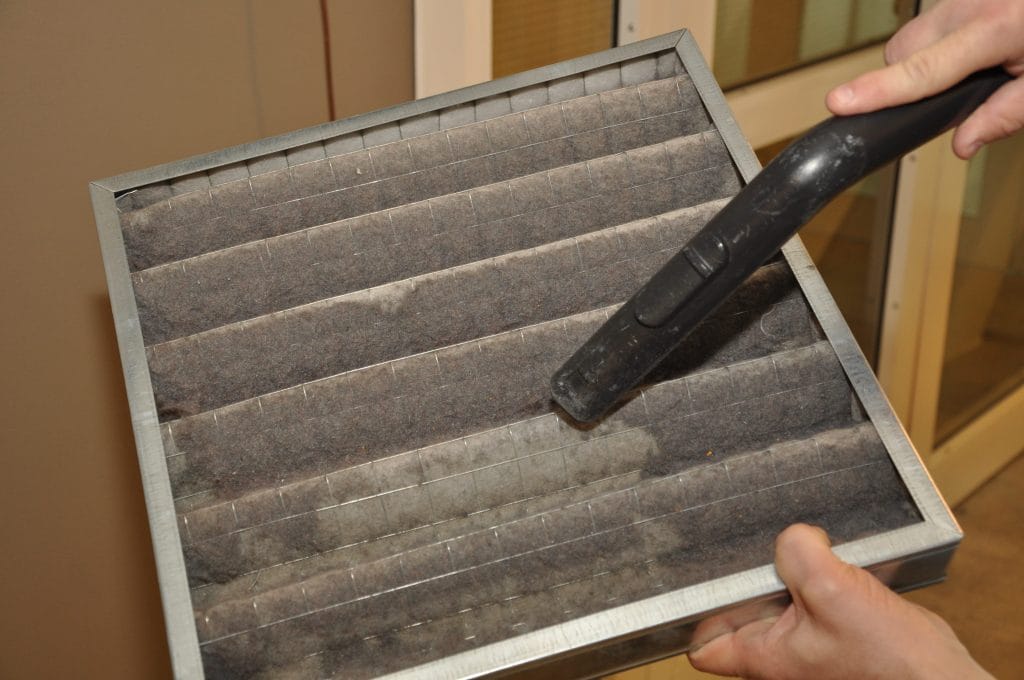

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Air filters play a crucial role in maintaining the quality of air inside

TL;DR Summary for Those in a Hurry: Showdown: HEPA or Activated Carbon? In today’s world, clean air is more important
We use cookies to improve your experience on our site. By using our site, you consent to cookies.
Manage your cookie preferences below:
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Google reCAPTCHA helps protect websites from spam and abuse by verifying user interactions through challenges.
Google Tag Manager simplifies the management of marketing tags on your website without code changes.
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us understand how visitors use our website.
Google Analytics is a powerful tool that tracks and analyzes website traffic for informed marketing decisions.
Service URL: policies.google.com (opens in a new window)