Selecting the right heating and cooling solution for your home can be quite a challenge, especially when faced with the decision between a heat pump and an air conditioning unit. Understanding Heat Pumps vs AC helps homeowners make an informed decision about efficiency, cost, and comfort. As a seasoned HVAC professional and owner of LC Heating and Air Conditioning in Hollywood, I understand the importance of making an informed decision to keep your home comfortable year-round. In this article, we’ll explore the fundamental differences between heat pumps and air conditioners, as well as their advantages and disadvantages, to help you determine which system best suits your needs.
Before diving into the pros and cons of each system, it’s essential to understand the basic functions of heat pumps and air conditioners.
Heat Pump
What is a Heat Pump?
A heat pump is an energy-efficient system that provides both heating and cooling. It works by transferring heat from one place to another using a refrigerant and a compressor. During the warmer months, a heat pump extracts heat from the inside of your home and releases it outside, thus cooling your home. In the colder months, it reverses this process, extracting heat from the outside air (or ground) and bringing it inside to warm your home.
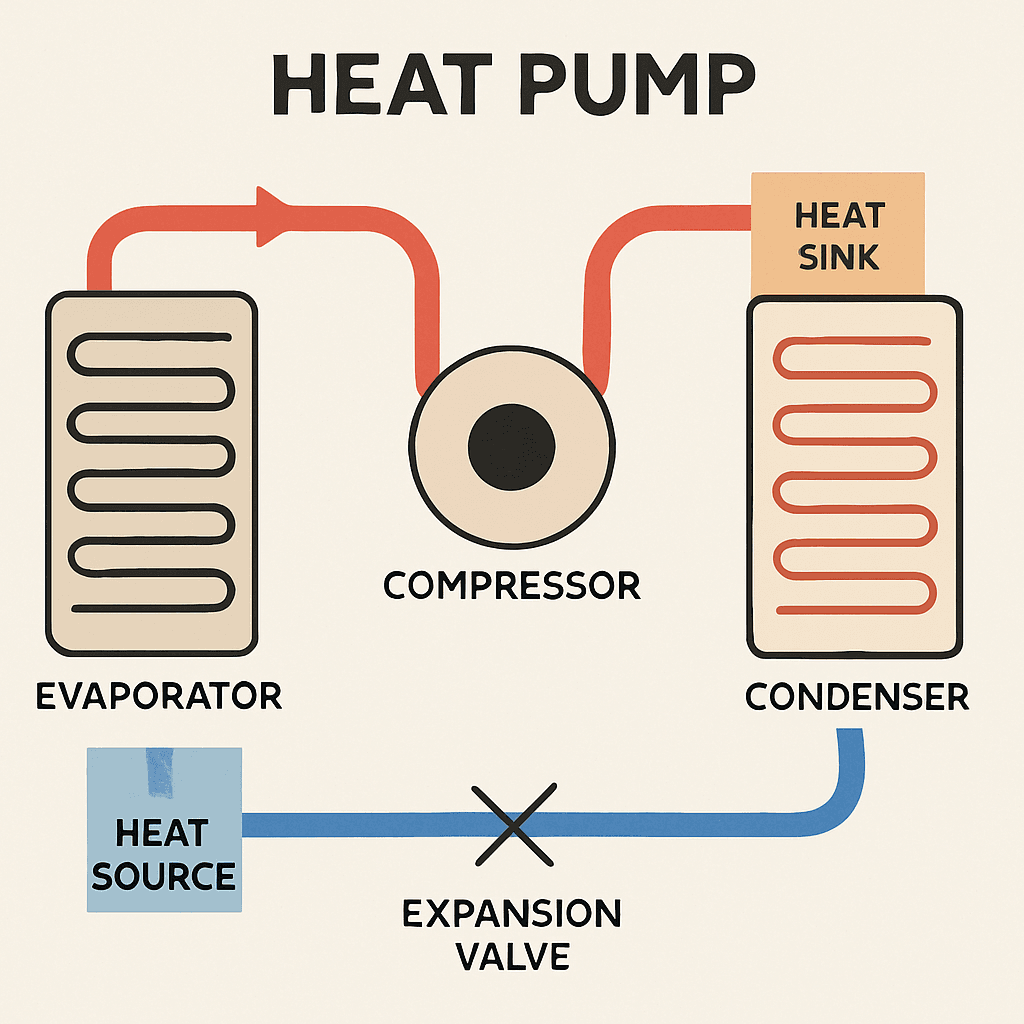
How Does a Heat Pump Work?
The operation of a heat pump involves a cycle of evaporation and condensation, driven by the refrigerant. This refrigerant absorbs heat from the air or ground, compresses it to increase the temperature, and then releases it indoors or outdoors, depending on the mode. The cycle is reversed when switching from cooling to heating, making it versatile for year-round use.
Types of Heat Pumps
There are several types of heat pumps, including air-source, ground-source (geothermal), and water-source models. Each type has specific applications and efficiencies. Air-source heat pumps are most common in residential settings due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of installation. Ground-source pumps, though more efficient, require a higher initial investment and space for installation.
Benefits of Heat Pumps
Heat pumps offer a sustainable alternative to traditional heating and cooling systems. They utilize renewable energy sources, which helps reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Their dual functionality also eliminates the need for separate systems, potentially saving space and maintenance costs.
Air Conditioner
What is an Air Conditioner?
An air conditioning unit, on the other hand, is designed solely for cooling purposes. It operates by absorbing heat from the indoor air and expelling it outside, thus lowering the temperature inside your home. Unlike a heat pump, an air conditioner does not provide heating; therefore, it is typically paired with a furnace or another heating system to maintain comfort during the cold season.
How Does an Air Conditioner Work?
An air conditioner functions by drawing warm air from inside a room, passing it over cold evaporator coils to absorb the heat, and then expelling the cooled air back into the room. The absorbed heat is released outside through condenser coils. This continuous cycle helps maintain a comfortable indoor temperature during hot weather.
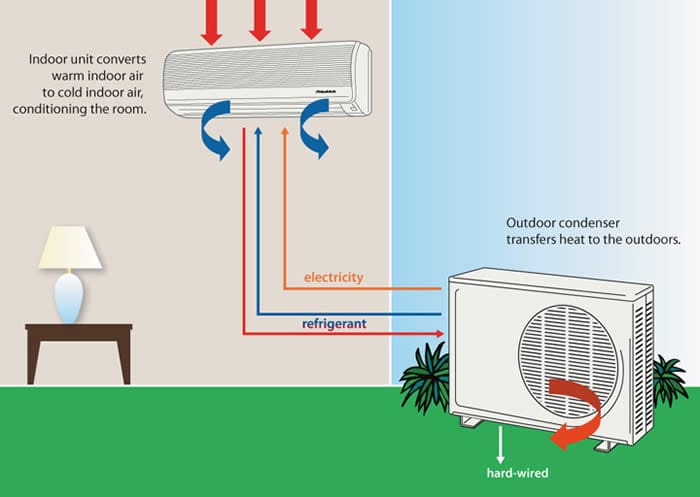
Types of Air Conditioning Units
Air conditioners come in various forms, including central air systems, window units, and portable models. Central air systems are ideal for cooling entire homes efficiently. Window units are suitable for cooling single rooms, while portable units offer flexibility for temporary cooling solutions.
Advantages of Air Conditioners
Air conditioning units are typically more effective in very hot climates where cooling is the primary concern. They often have lower initial costs compared to heat pumps, making them attractive for homeowners looking for budget-friendly options. Additionally, advancements in technology have improved their energy efficiency and cooling capabilities.
Key Differences Between Heat Pumps and Air Conditioners
When choosing between a heat pump and an air conditioning unit, it’s crucial to consider several key factors.
Energy Efficiency
Heat pumps are generally more energy-efficient compared to traditional air conditioners, primarily because they move heat rather than generate it. This efficiency can lead to lower utility bills, making heat pumps an attractive option for homeowners who prioritize energy savings.
Heat Pumps and Energy Consumption
Heat pumps can achieve efficiencies up to 300%, meaning they can produce three times the energy they consume. This is largely due to their ability to transfer existing heat rather than create it. Homeowners often see significant reductions in their energy bills, especially in moderate climates.
Air Conditioners and Energy Use
Air conditioners, while efficient in cooling, typically have a lower efficiency rating compared to heat pumps. They consume more energy as they are limited to cooling functions only. However, modern air conditioners have seen improvements in SEER ratings, making them more competitive in energy efficiency.
Comparing Long-term Savings
When evaluating long-term savings, it’s important to consider not just the initial installation cost but also the ongoing energy expenses. Heat pumps, despite potentially higher upfront costs, may offer greater savings in the long run due to their efficiency and dual functionality.
Climate Suitability
The effectiveness of a heat pump can depend significantly on your local climate. In regions with mild winters, heat pumps are highly efficient. However, in areas with extremely cold winters, their efficiency may decrease as they struggle to extract sufficient heat from the cold outdoor air. In such climates, a central air conditioning unit paired with a furnace might be a more suitable option.
Heat Pumps in Mild Climates
In areas with moderate temperatures, heat pumps can perform exceptionally well throughout the year. They provide efficient heating and cooling without the need for additional systems, making them an all-in-one solution for homes in such regions.
Challenges in Cold Climates
In colder climates, heat pumps may struggle as temperatures drop significantly. The efficiency decreases as the system works harder to extract minimal heat from the outside air. In these scenarios, supplemental heating may be required, such as electric resistance heaters or gas furnaces.
Air Conditioners in Hot Climates
Air conditioners excel in hot climates where cooling is the primary concern. They provide reliable and efficient cooling during scorching summers. Pairing them with a separate heating system, like a furnace, ensures comfort throughout the year.
Installation and Maintenance Costs
Both heat pumps and air conditioners have comparable installation costs, but a heat pump’s dual functionality could lead to cost savings over time. However, because a heat pump operates year-round, it may require more frequent maintenance compared to a seasonal air conditioning unit.
Initial Installation Costs
The installation costs of heat pumps and air conditioners can vary based on the type and size of the system. Generally, heat pumps have a higher initial cost due to their dual functionality and potential need for additional components, such as ductwork.
Maintenance Considerations
Heat pumps, operating year-round, might require more frequent maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Regular checks on refrigerant levels, compressor function, and system cleanliness are crucial. Air conditioners, used seasonally, may have less wear and tear but still benefit from annual maintenance.
Long-term Cost Implications
While heat pumps may have higher upfront costs, their energy efficiency and ability to serve as both a heater and cooler can lead to long-term savings. Air conditioners, with potentially lower initial costs, might incur higher energy expenses, especially if paired with less efficient heating systems.
Pros and Cons of Heat Pumps and Air Conditioners
Heat Pumps
Pros:
- Dual functionality for heating and cooling.
- Energy-efficient operation.
- Lower carbon footprint.
Additional Pros of Heat Pumps
Heat pumps provide a cleaner alternative to traditional heating systems by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. They are ideal for homes aiming for sustainability. Additionally, newer models offer advanced features like variable-speed compressors and smart thermostats, enhancing comfort and efficiency.
Cons:
- May be less efficient in extremely cold climates.
- Higher initial installation costs compared to a standalone AC unit.
Additional Cons of Heat Pumps
Heat pumps may require a backup heating source in extremely cold weather, adding to the overall system complexity and cost. The initial installation process can be more complex due to potential ductwork modifications or additional components required for optimal performance.
Air Conditioners
Pros:
- Efficient cooling performance in hot climates.
- Typically lower upfront costs compared to heat pumps.
Additional Pros of Air Conditioners
Air conditioners offer specialized cooling, often delivering faster results in hot conditions. They are easier to install and have a wide range of options for different budgets and room sizes. Portable and window units provide flexibility for renters or temporary cooling needs.
Cons:
- Requires a separate heating system for winter months.
- Generally less energy-efficient compared to heat pumps.
Additional Cons of Air Conditioners
Air conditioners are limited to cooling, necessitating additional heating systems, which can increase overall energy consumption. In some cases, air conditioners may also contribute to higher humidity levels indoors if not properly maintained or sized.
Making the Right Choice for Your Home
When deciding between a heat pump and an air conditioning unit, consider your specific needs, budget, and climate conditions. Here are a few pointers to guide you:
Evaluating Your Climate
- If you live in a region with mild winters and want a single system to handle both heating and cooling, a heat pump may be the ideal choice.
- If your area experiences harsh winters and you already have a reliable heating system, an air conditioner could be a more practical and economical solution.
Understanding Seasonal Needs
Consider the duration and intensity of your local weather patterns. Homes in transitional climates, where both heating and cooling are required at different times of the year, can benefit significantly from the versatility of a heat pump.
Budget Considerations
- Consider the long-term energy savings of a heat pump versus the potentially lower initial costs of an air conditioner.
Assessing Initial vs. Long-term Costs
Factor in not only the initial purchase and installation costs but also the operational costs over time. Energy-efficient systems may have higher upfront expenses but can lead to considerable savings on utility bills over the lifespan of the system.
Future-proofing Your Home
Evaluate the potential for future energy costs and environmental regulations. Investing in energy-efficient systems like heat pumps can help future-proof your home against rising energy prices and stricter environmental standards.
Conclusion: Heat Pumps vs AC
Choosing between a heat pump and an air conditioning unit is not a one-size-fits-all decision. By understanding the differences and evaluating your specific requirements, you can make an informed choice that ensures comfort and efficiency for your home.
If you have any questions or need assistance in selecting the right system, feel free to contact us at LC Heating and Air Conditioning in Hollywood. We’re here to help you make the best decision for your home and ensure your HVAC system runs smoothly all year long. You can reach us at (818) 858-7080.
Remember, when it comes to heating and cooling your home, trust, quality, and customer satisfaction are our top priorities. Let us help you create the perfect indoor environment for you and your family.


